Options trading is a fascinating but complex financial instrument that offers flexibility, leverage, and the potential for significant returns. For beginners, understanding the basics of options and utilizing proven, accessible strategies can be the key to success. In this article, we’ll dive deep into essential options trading strategies, with practical explanations and real-life examples to help you get started.
Understanding the Basics of Options

Before delving into strategies, let’s ensure that the fundamentals are clear.
Options are financial derivatives, which means their value is derived from an underlying asset such as stocks, commodities, or indices. There are two primary types of options:
- Call Options: These give the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to buy an underlying asset at a specific price (strike price) before a certain date (expiration date).
- Put Options: These give the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to sell an underlying asset at a predetermined price before the expiration date.
To execute a strategy, it’s essential to understand the underlying asset’s movements, the concept of strike prices, expiration dates, and the factors affecting an option’s price, such as volatility and time decay.
Why Trade Options?
Options provide opportunities that other forms of trading don’t. The advantages include:
- Leverage: With options, you can control a large amount of stock with a smaller initial investment. This means greater potential returns.
- Income Generation: Options can generate additional income through strategies like selling calls and puts.
- Risk Management: When used correctly, options can protect other investments in your portfolio from downside risk, a strategy known as hedging.
- Flexibility: Options can profit in all kinds of market conditions: bullish, bearish, or sideways.
Understanding the power of options can help you decide how to use them as part of your broader trading strategy.
Beginner-Friendly Options Strategies

There are many strategies that cater to different market conditions and risk appetites. Here, we’ll focus on a few strategies that are particularly suitable for beginners. These strategies are easy to understand and provide real-life examples to show how they can be implemented successfully.
1. Buying Call Options: The Bullish Strategy
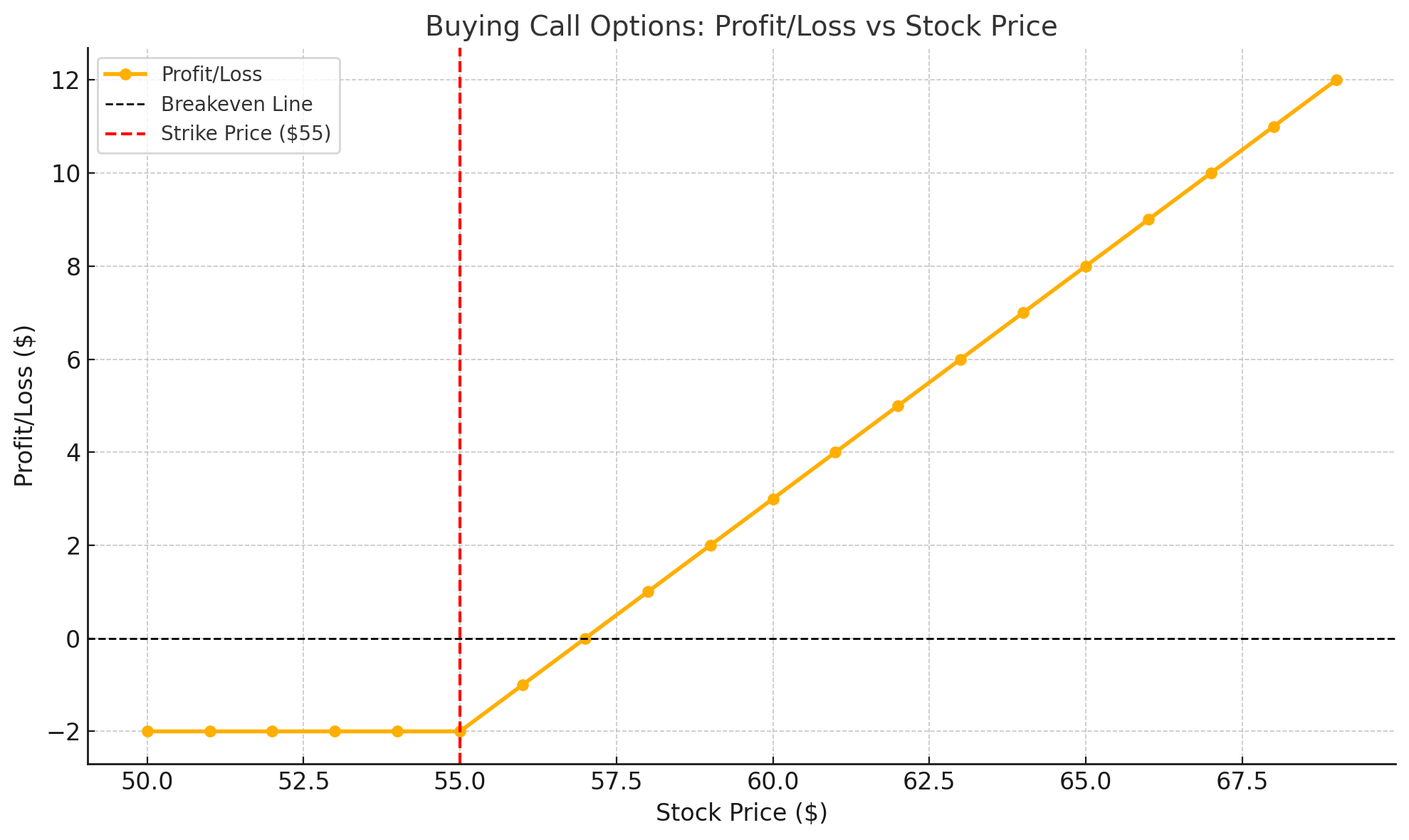
Buying call options is one of the most straightforward strategies and ideal for traders who expect the price of an underlying asset to rise. When you buy a call option, you gain the right to buy the stock at the strike price within a specified period. If the price of the asset rises, the value of the call option also increases.
How it works:
- Suppose a stock is trading at $50, and you buy a call option with a strike price of $55 for a $2 premium.
- If the stock rises to $60, your call option allows you to buy the stock at $55.
- Your profit would be the difference between the strike price and the stock price ($60 – $55), minus the premium paid ($2), giving you a profit of $3 per share.
Why it works:
This strategy works when the market is trending upwards, and you believe the asset’s price will increase substantially within the option’s timeframe. The key benefit of buying calls is that your potential profit is unlimited, while your risk is limited to the premium you paid for the option.
Real-Life Example:
A beginner trader could see an uptrend in the technology sector, specifically in a company like Apple (AAPL). If Apple’s stock is trading at $150, a trader may buy a call option with a strike price of $160 for $5. If Apple’s stock rises to $170 before the option expires, the trader can exercise the call, buying the stock at $160, selling it at $170, and making a profit of $10 minus the $5 premium, totaling a $5 profit per share.
2. Buying Put Options: The Bearish Strategy
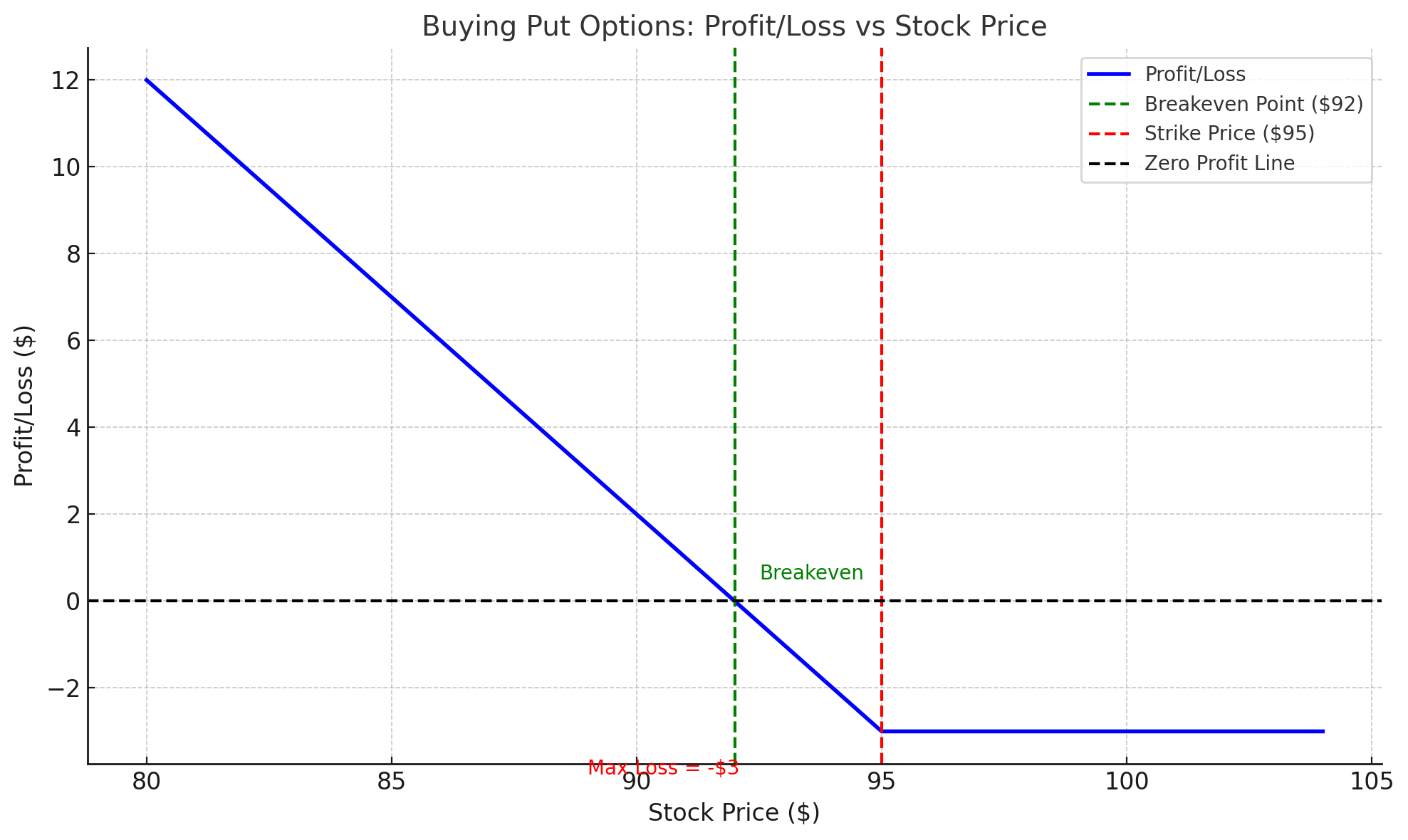
While buying call options works when the market is bullish, buying put options is used when traders anticipate the price of an asset to decline. When you buy a put option, you gain the right to sell the underlying asset at a specific price (strike price) by the expiration date.
How it works:
- Imagine a stock is trading at $100, and you buy a put option with a strike price of $95 for a $3 premium.
- If the stock price drops to $90, your put option allows you to sell the stock at $95, and you make a profit of $5 (the difference between the strike price and the stock price), minus the premium ($3).
- Your net profit would be $2 per share.
Why it works:
This strategy is ideal in a bearish market or when you expect a specific stock to drop in value. It allows you to profit from a decline in the asset’s price while keeping your risk limited to the premium you paid.
Real-Life Example:
In 2020, during the early stages of the COVID-19 pandemic, many traders used put options to profit from the sharp declines in the stock market. For instance, if a stock like Boeing (BA) was trading at $200, and a trader believed it would drop due to travel restrictions, they could purchase a put option with a strike price of $190 for a premium of $5. If the stock price fell to $170, the trader would profit by exercising the option and selling the stock at the higher strike price of $190.
3. Covered Calls: Income Generation
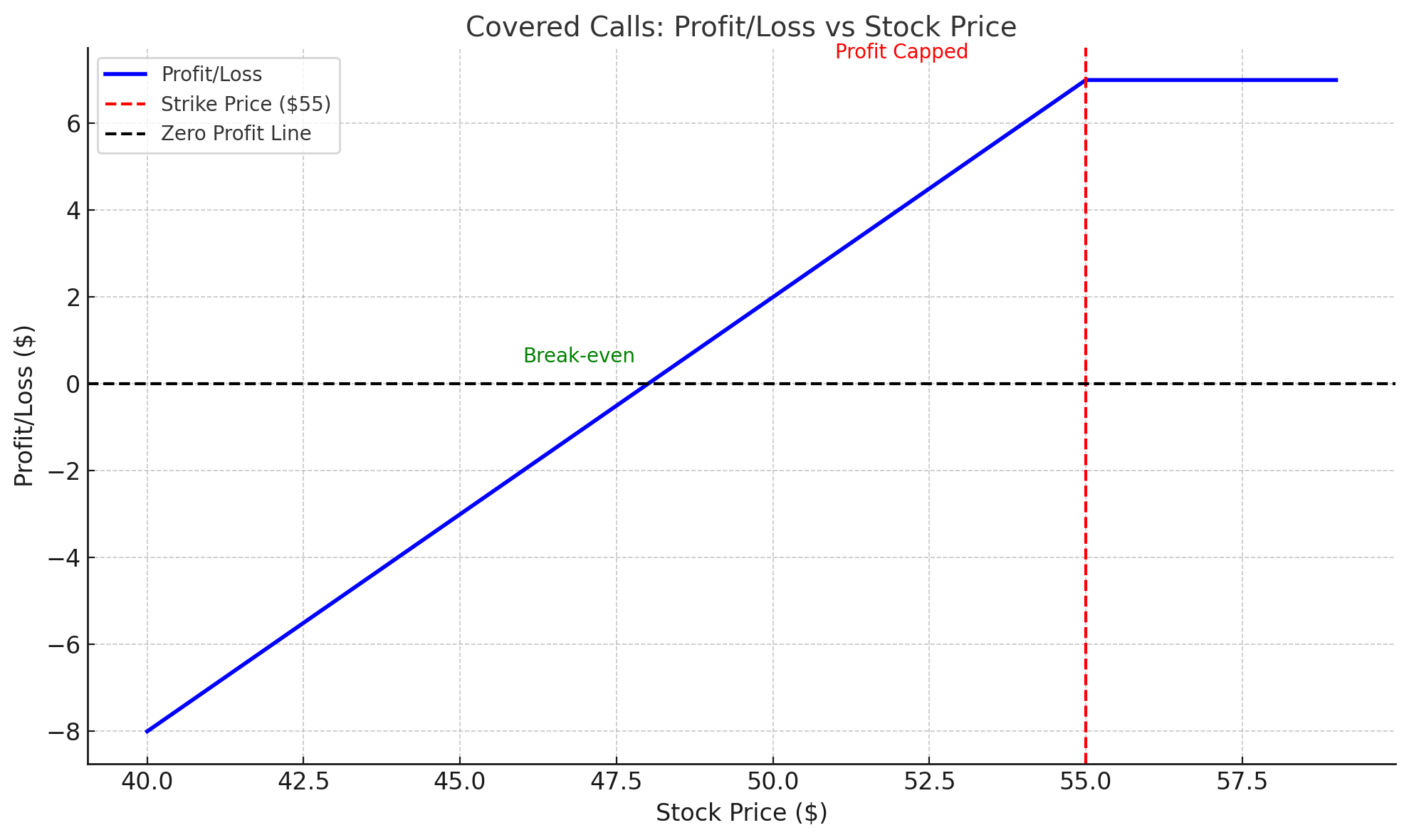
For traders who own a stock and want to generate additional income, a covered call strategy can be effective. This strategy involves selling a call option on stocks you already own. By doing so, you receive a premium from the sale of the option, which you keep as income.
How it works:
- Suppose you own 100 shares of a stock priced at $50 per share. You sell a call option with a strike price of $55 for a premium of $2.
- If the stock stays below $55, you keep the premium, and the call expires worthless.
- If the stock price rises above $55, you must sell your shares at $55, but you still keep the $2 premium, which boosts your return on the sale.
Why it works:
The covered call strategy works best in sideways or moderately bullish markets. The trader benefits from the premium income and potential stock appreciation, but their upside is limited to the strike price of the option. The primary risk is that the stock may rise well above the strike price, and the trader will miss out on potential gains.
Real-Life Example:
Imagine owning 100 shares of stock XYZ, which is trading at $40 per share. You sell a call option with a strike price of $45 for a premium of $3. If the stock price doesn’t rise above $45, you keep the $3 premium, and the option expires. However, if the stock goes up to $50, you are obligated to sell the stock at $45, but still pocket the $3 premium.
4. The Protective Put: A Hedging Strategy
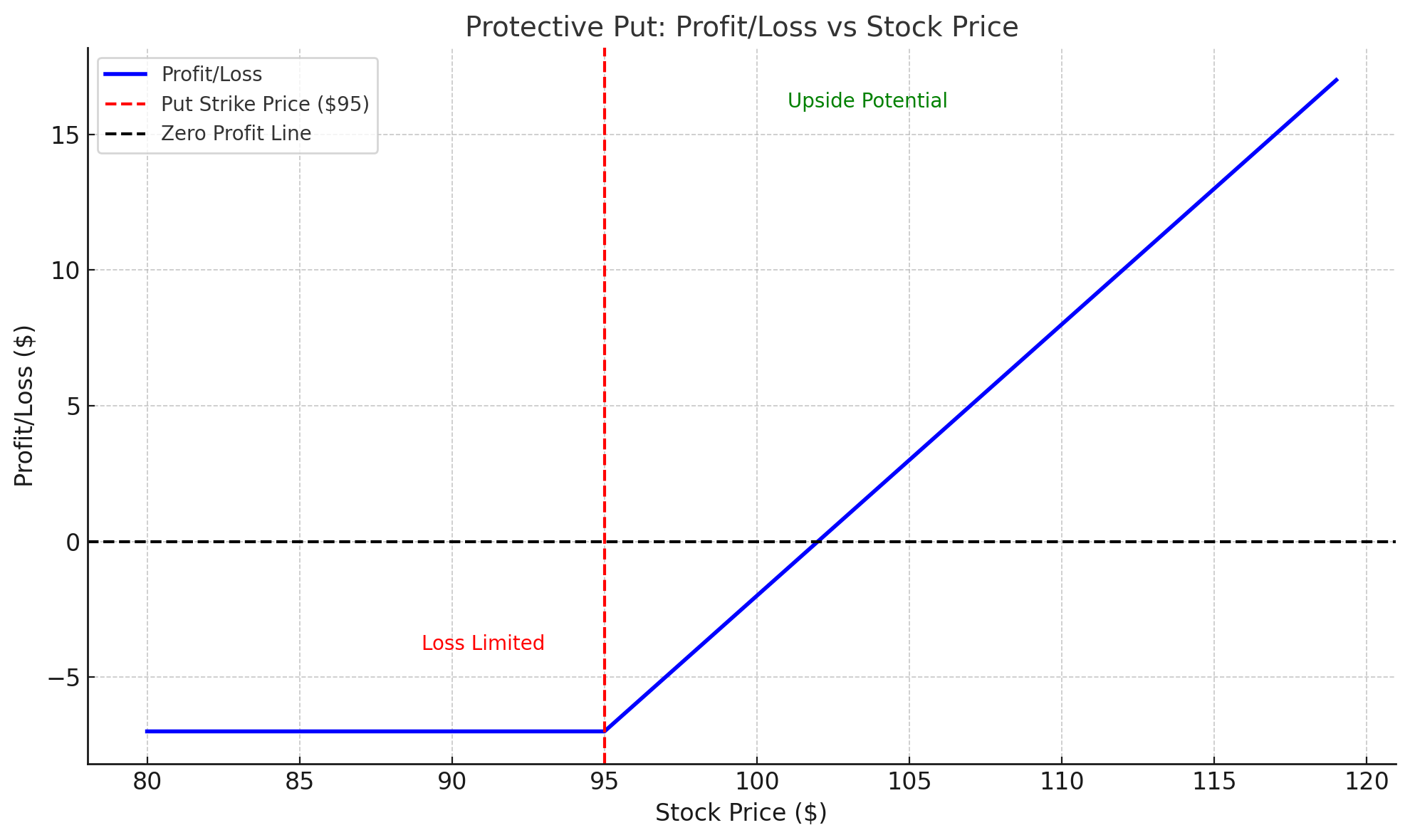
A protective put is a risk-management strategy used by traders who want to safeguard their existing stock positions. By buying a put option on a stock you already own, you can hedge against potential losses if the stock price declines.
How it works:
- If you own shares of a stock trading at $100, and you’re concerned the price might fall, you can buy a put option with a strike price of $95 for $2.
- If the stock price drops to $90, the put option increases in value, and you can sell the stock at the $95 strike price.
- This strategy limits your losses while allowing you to continue benefiting from any upside potential.
Why it works:
The protective put strategy is ideal for mitigating risk, especially if you have long-term holdings and want to protect them from short-term downturns. It allows you to maintain the upside potential of the stock while having a safety net in place.
Real-Life Example:
Imagine holding shares in a company like Amazon (AMZN) trading at $3,200. If you believe there’s a potential market correction, you might buy a protective put with a $3,100 strike price for $100. If the stock falls to $2,800, the put option increases in value, offsetting the loss in the stock.
Proven Strategies and Key Considerations
While beginner-friendly strategies like buying calls and puts, selling covered calls, and using protective puts are easy to grasp, the most successful traders also employ a blend of several strategies. One popular strategy is the iron condor, which involves selling an out-of-the-money call and put while simultaneously buying further out-of-the-money options to limit risk. This strategy is ideal for traders expecting low volatility.
Key Tips for Beginners:
- Start Small: Begin with strategies that offer defined risk, such as buying calls and puts, and gradually scale as you gain experience.
- Educate Yourself: Continuously learn from trusted resources, and don’t be afraid to paper trade before committing real money.
- Understand Market Conditions: Different strategies work better in different market environments, so make sure to align your strategy with market trends.
- Manage Risk: Options are leveraged instruments, so always know your maximum potential loss before entering a trade.
Conclusion
Options trading offers tremendous potential for profits, but it’s essential to approach it with a solid understanding of the strategies and risks involved. By starting with simple, proven strategies such as buying calls and puts, selling covered calls, and using protective puts, you can begin your journey in options trading with confidence. As you progress, you can explore more complex strategies like iron condors and spreads to further enhance your trading toolkit.