Options trading can be a powerful tool for maximizing profits while managing risk. While beginners often focus on basic strategies like buying calls or puts, intermediate traders can employ more sophisticated techniques to enhance profitability and navigate diverse market conditions. This article delves into the top intermediate options strategies, providing in-depth explanations and insights into how to use them effectively.
What Are Options?
Options are financial derivatives that give traders the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset at a specified price before a certain date. These assets can include stocks, ETFs, indices, and more.
- Call Option: Gives the right to buy the underlying asset.
- Put Option: Gives the right to sell the underlying asset.
Key Concepts to Understand Before Using Intermediate Strategies

- Intrinsic and Extrinsic Value
- Intrinsic Value: The actual value of the option if exercised immediately.
- Extrinsic Value: The time value or premium above the intrinsic value, influenced by time to expiration, volatility, and interest rates.
- Implied Volatility (IV)
Implied volatility measures the market’s expectations of future price movement. High IV increases options premiums, while low IV reduces them. Understanding IV is crucial for deploying intermediate strategies effectively. - Time Decay (Theta)
Options lose value as they approach expiration, making time decay a significant factor in strategies involving short-term contracts. - Delta, Gamma, Vega, and Rho
The “Greeks” measure different risk factors in options trading. Mastery of these metrics helps traders predict and manage options behavior.
Top Intermediate Options Strategies
1. Covered Call Strategy
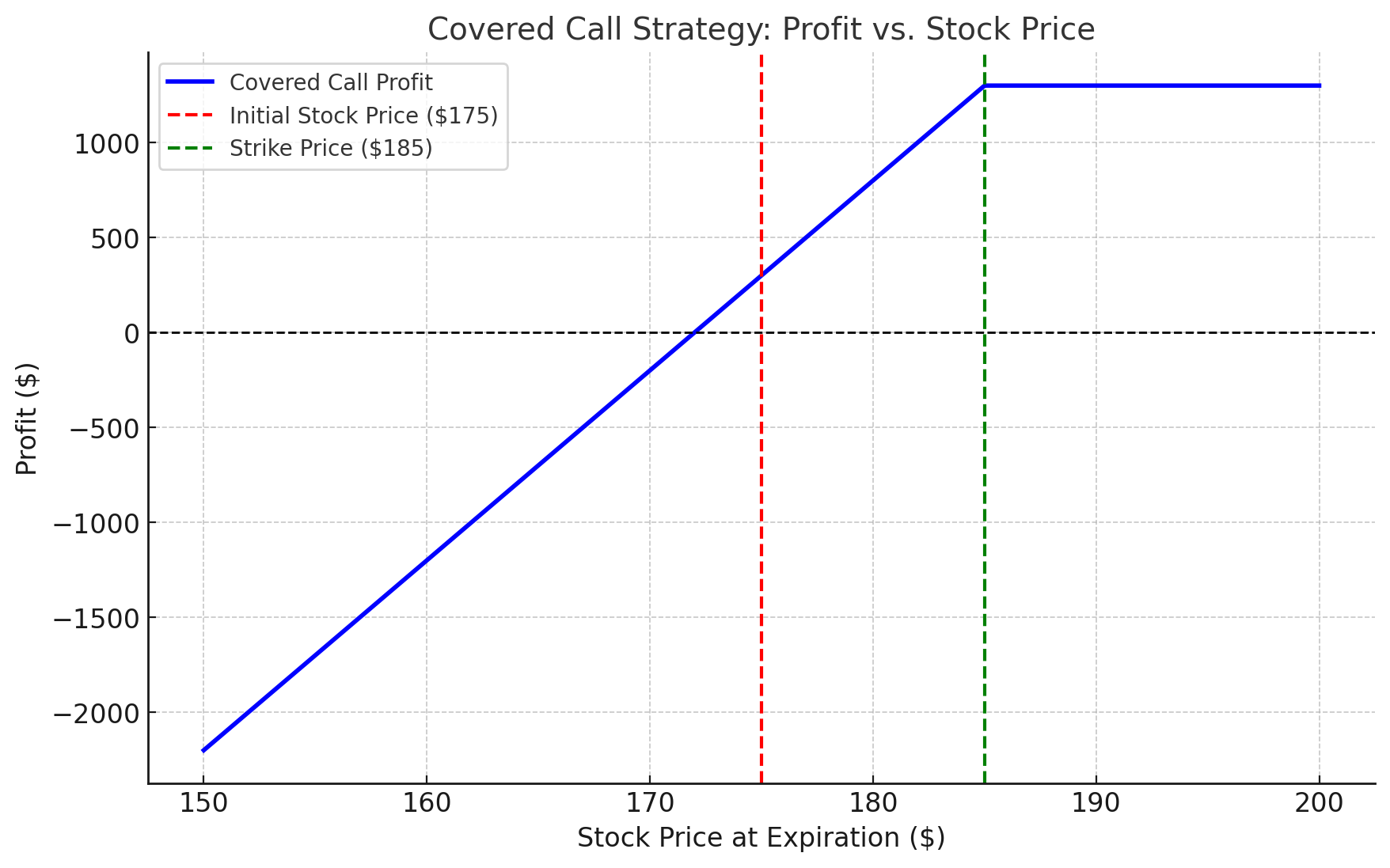
Objective: Generate income on a stock you already own.
How It Works
- Buy at least 100 shares of a stock.
- Sell a call option with a strike price higher than the current stock price.
- Collect the premium. If the stock’s price rises above the strike price, the shares may be sold at the strike price, but you keep the premium.
Example
- You own 100 shares of Apple (AAPL) at $175/share.
- You sell a call option with a strike price of $185 expiring in one month for a $3 premium.
- Scenario 1: If AAPL stays below $185, you keep the $3/share premium ($300 total) and retain your stock.
- Scenario 2: If AAPL rises above $185, your shares are sold at $185, but you still keep the premium.
Best Market Conditions
- Neutral to slightly bullish markets.
Advantages
- Generates consistent income from premiums.
- Offers partial downside protection.
Risks
- Limits upside potential if the stock price skyrockets.
- Retains full downside risk if the stock price declines significantly.
2. Cash-Secured Put Strategy
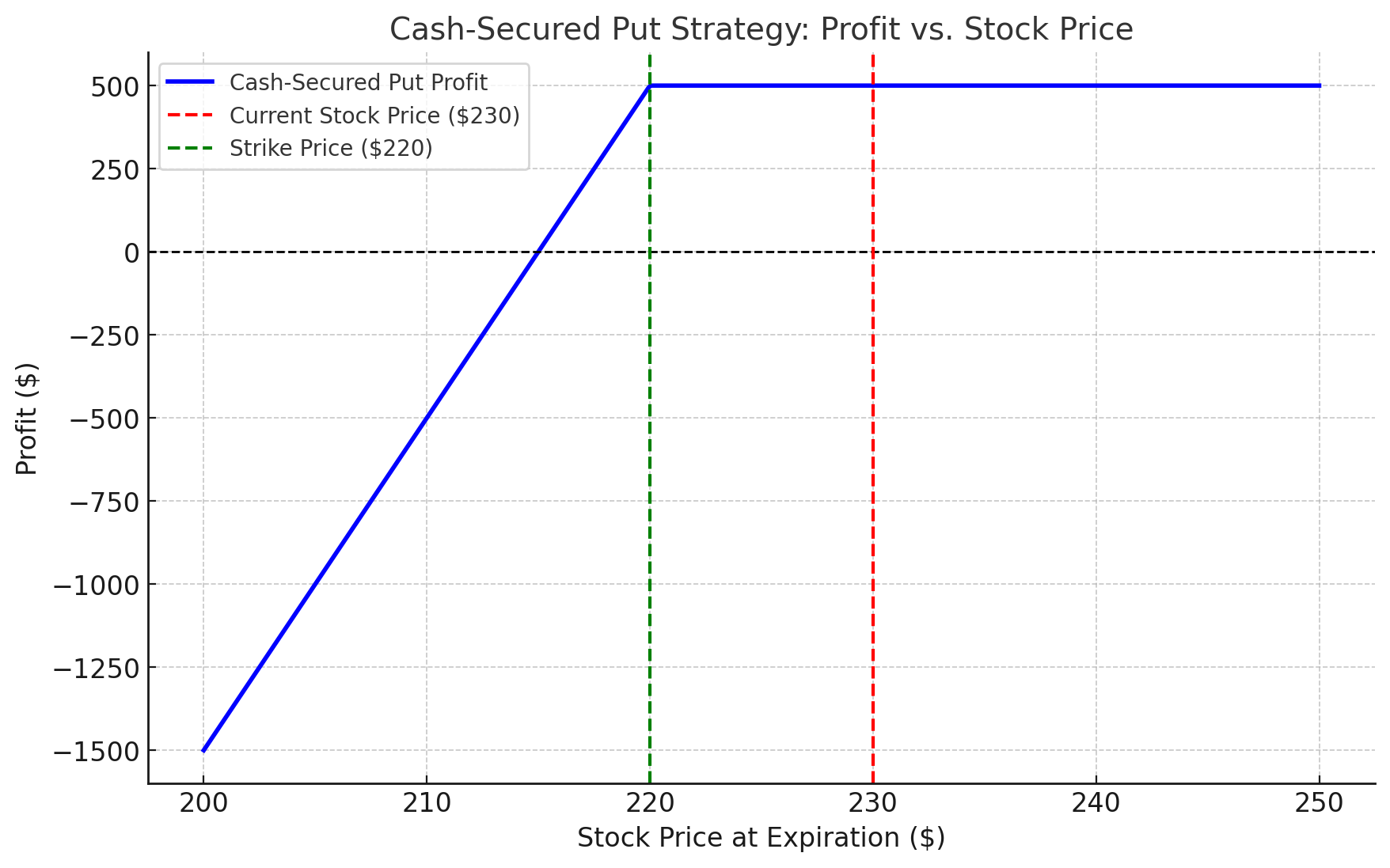
Objective: Buy a stock at a discount or generate income.
How It Works
- Sell a put option at a strike price below the current stock price.
- Keep enough cash in your account to buy the stock if the option is exercised.
Example
- Tesla (TSLA) is trading at $230.
- You sell a put option with a strike price of $220 for a $5 premium.
- Scenario 1: If TSLA stays above $220, you keep the $5/share premium ($500 total).
- Scenario 2: If TSLA falls below $220, you are obligated to buy the shares at $220, effectively purchasing at $215 when accounting for the premium.
Best Market Conditions
- Neutral to slightly bearish markets.
Advantages
- Income generation.
- Allows you to buy the stock at a lower effective price.
Risks
- Requires cash to secure the trade.
- Obligation to buy the stock even if the price drops significantly.
3. Vertical Spreads
Bull Call Spread
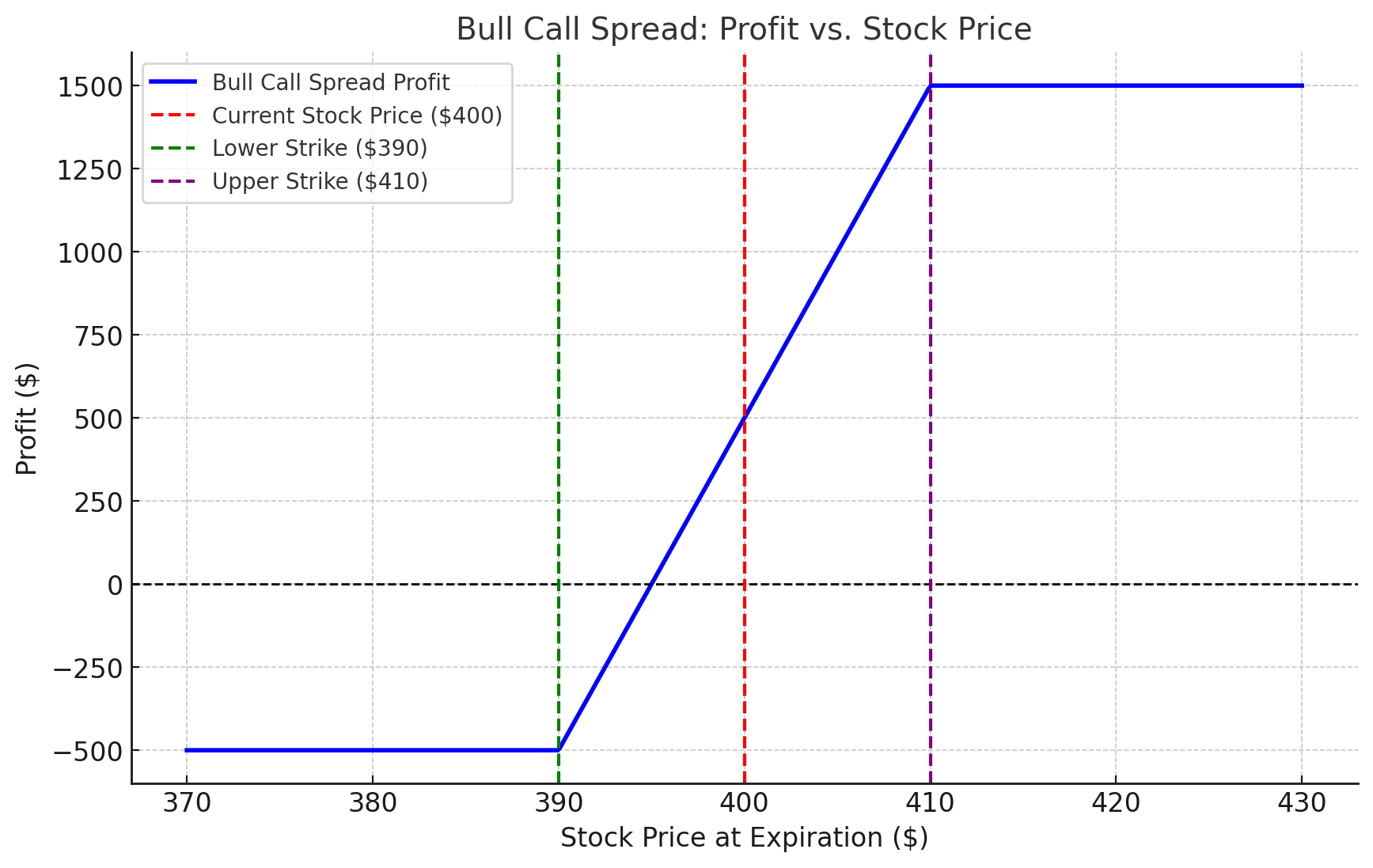
Objective: Profit from a moderate price increase.
How It Works
- Buy a call option at a lower strike price.
- Sell a call option at a higher strike price (same expiration date).
Example
- Netflix (NFLX) is trading at $400.
- You buy a call at a $390 strike price for $15 and sell a call at $410 for $10.
- Net Cost: $15 – $10 = $5/share ($500 total).
- Scenario 1: If NFLX rises to $405 at expiration, your profit is $5/share minus the initial cost.
- Scenario 2: If NFLX is below $390, the options expire worthless, and your loss is limited to the $500 premium.
Bear Put Spread
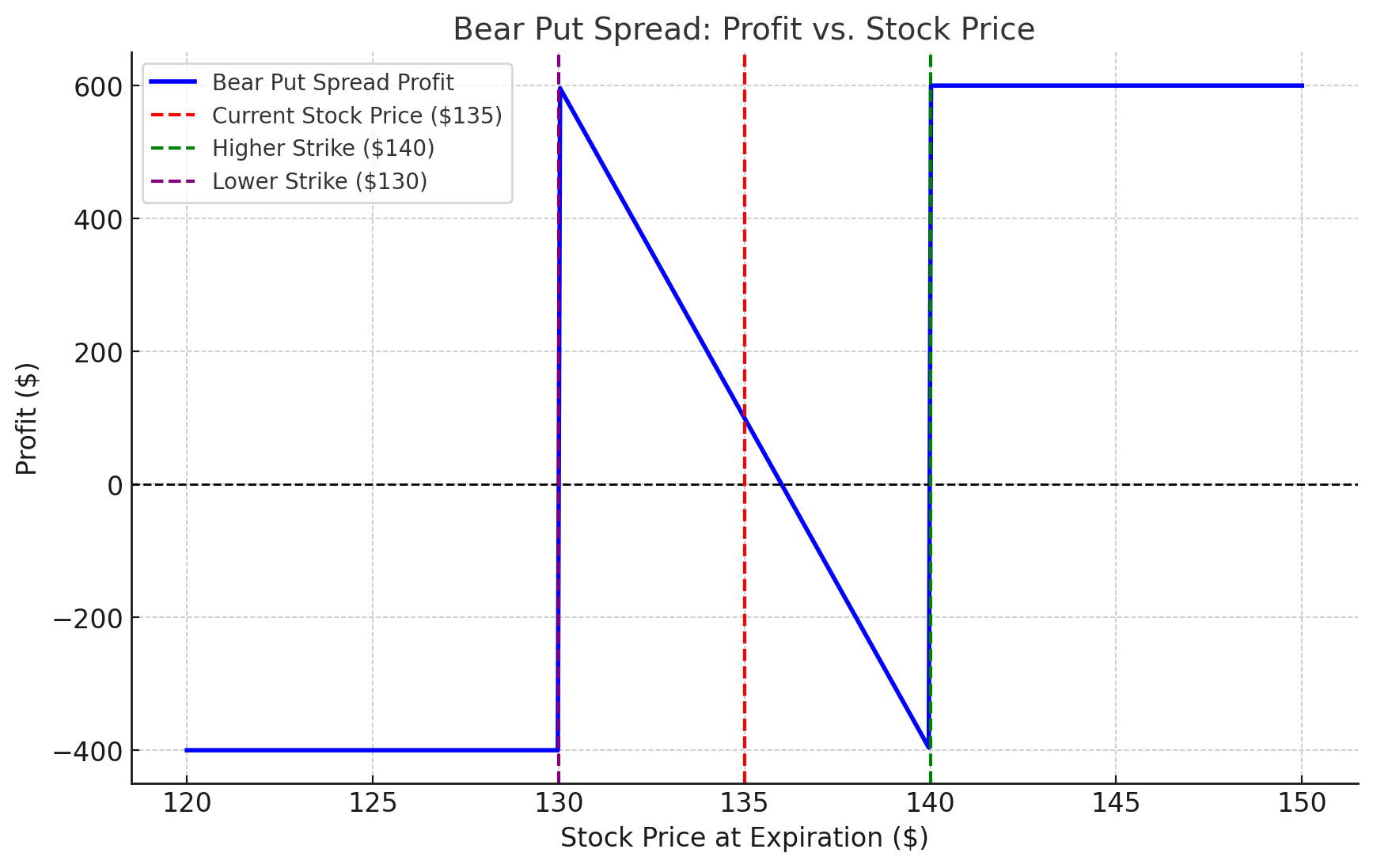
Objective: Profit from a moderate price decline.
How It Works
- Buy a put option at a higher strike price.
- Sell a put option at a lower strike price (same expiration date).
Example
- Amazon (AMZN) is trading at $135.
- You buy a put at $140 for $8 and sell a put at $130 for $4.
- Net Cost: $4/share ($400 total).
- Scenario 1: If AMZN falls to $125, your profit is $6/share minus the initial cost.
- Scenario 2: If AMZN stays above $140, your loss is limited to the $400 premium.
4. Iron Condor Strategy
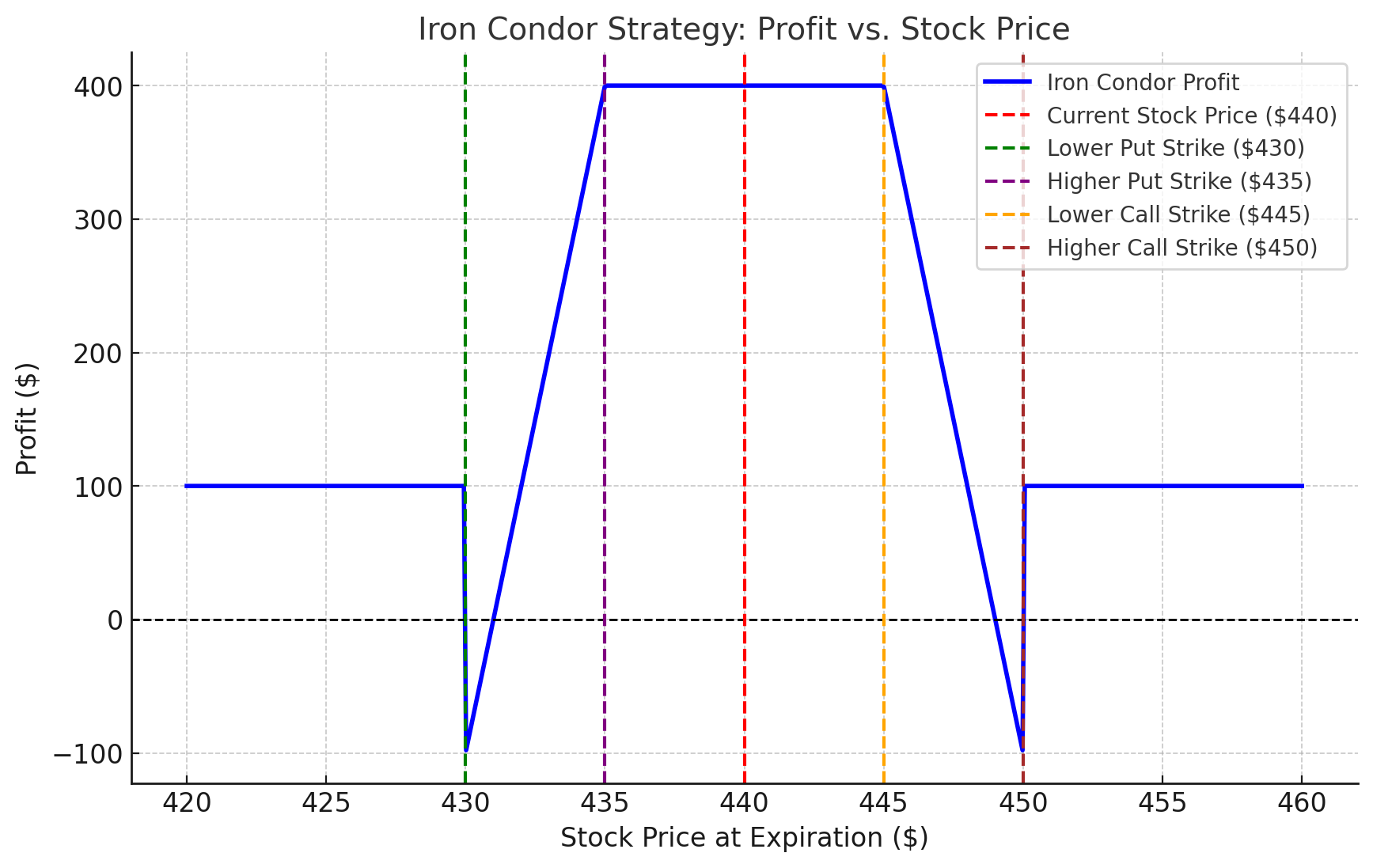
Objective: Profit from low volatility.
How It Works
- Combine a bull put spread and a bear call spread.
- Sell a put at a lower strike price and buy a put at an even lower strike price.
- Sell a call at a higher strike price and buy a call at an even higher strike price.
Example
- SPY ETF is trading at $440.
- You sell a $435 put and buy a $430 put.
- You sell a $445 call and buy a $450 call.
- Scenario 1: If SPY remains between $435 and $445, you keep all premiums.
- Scenario 2: If SPY moves significantly outside this range, your loss is capped.
Best Market Conditions
- Neutral markets with low volatility.
Advantages
- High probability of success.
- Limited risk and reward.
5. Butterfly Spread
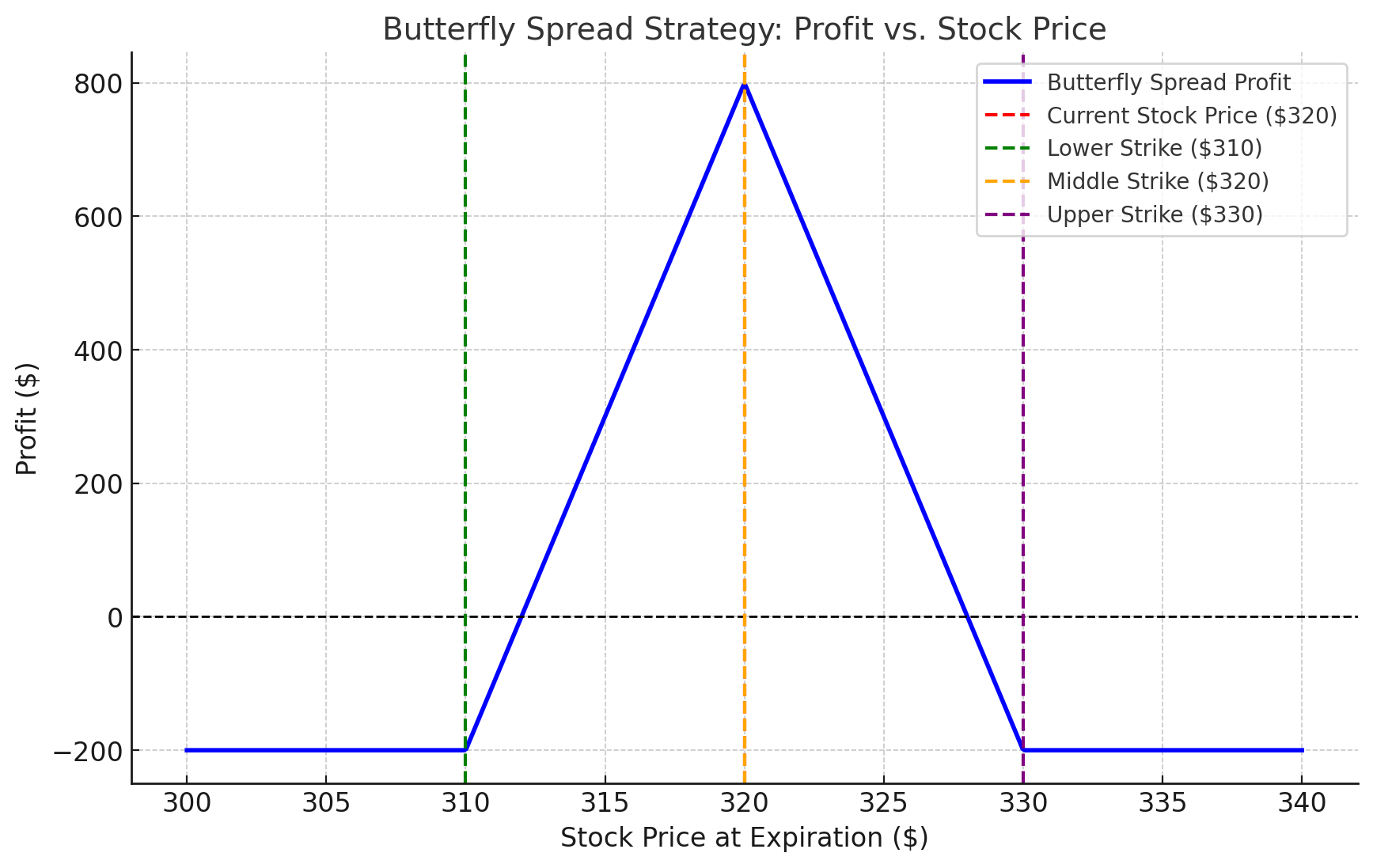
Objective: Profit from minimal price movement.
How It Works
- Buy a call at a lower strike price.
- Sell two calls at a middle strike price.
- Buy a call at a higher strike price (all same expiration date).
Example
- Microsoft (MSFT) is trading at $320.
- You buy a $310 call, sell two $320 calls, and buy a $330 call.
- Net Cost: $2/share ($200 total).
- Scenario 1: If MSFT stays around $320 at expiration, you maximize profits.
- Scenario 2: If MSFT moves significantly, your loss is capped at $200.
6. Straddles and Strangles
Straddle
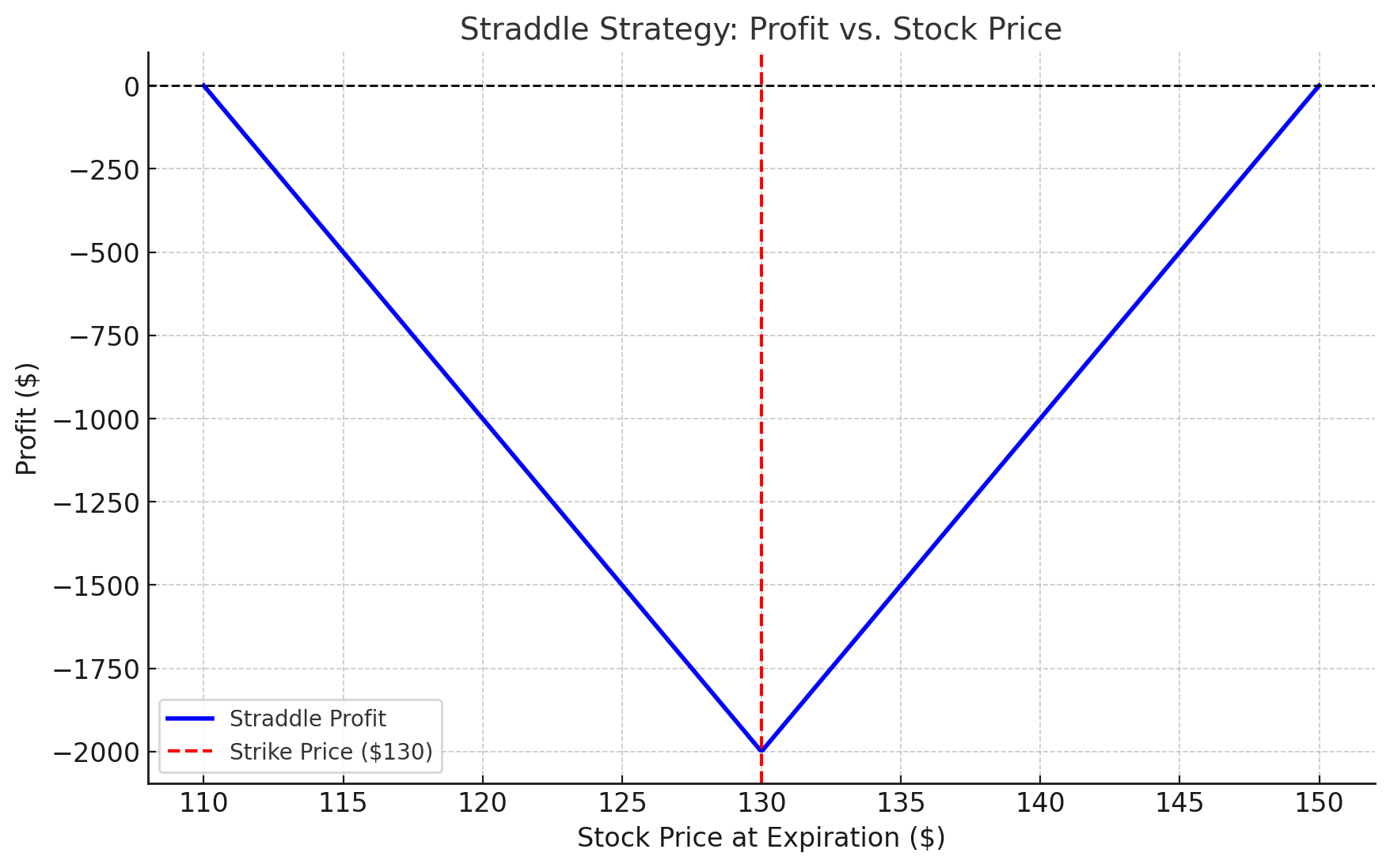
Objective: Profit from significant price movement in either direction.
How It Works
- Buy a call and a put option with the same strike price and expiration.
Example
- Google (GOOGL) is trading at $130.
- You buy a $130 call for $5 and a $130 put for $5.
- Net Cost: $10/share ($1,000 total).
- Scenario 1: If GOOGL moves to $140 or $120, one option gains enough to offset the loss of the other and the premium.
- Scenario 2: If GOOGL stays near $130, both options expire worthless, and your loss is $1,000.
Strangle
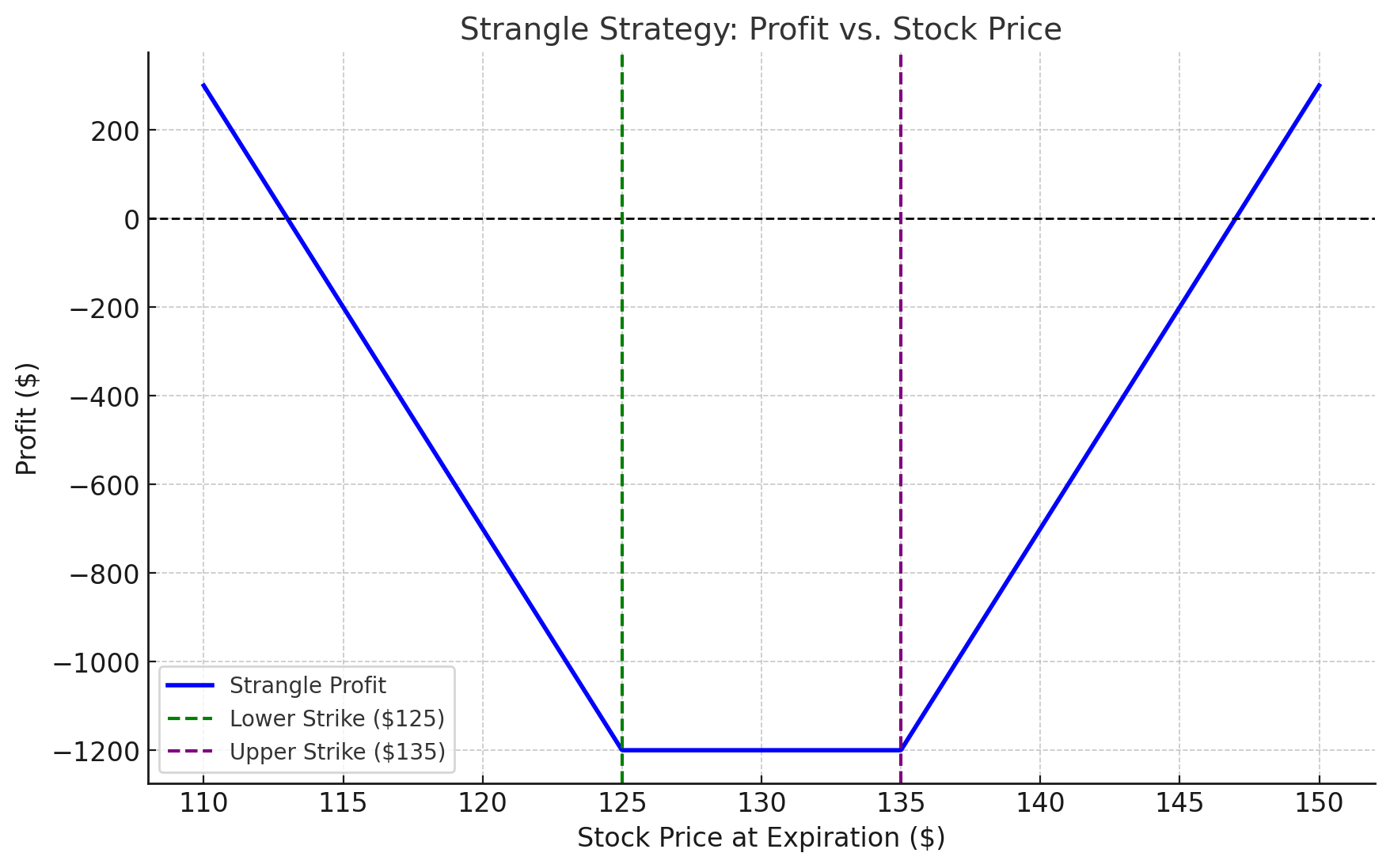
Objective: Similar to a straddle but uses out-of-the-money options for lower cost.
Example
- GOOGL is trading at $130.
- You buy a $125 put for $3 and a $135 call for $3.
- Net Cost: $6/share ($600 total).
- Scenario 1: Significant price movement results in profit.
- Scenario 2: Minimal price movement leads to a $600 loss.
7. Calendar Spread
Objective: Profit from differences in time decay.
How It Works
- Sell a short-term option.
- Buy a longer-term option at the same strike price.
Example
- Intel (INTC) is trading at $50.
- You sell a $50 call expiring in one week for $2.
- You buy a $50 call expiring in one month for $4.
- Net Cost: $2/share ($200 total).
- Scenario 1: If INTC remains near $50 after the first option expires, you profit as the longer-term option retains value.
Key Considerations for Intermediate Strategies
- Risk Management
- Always use defined-risk strategies when possible.
- Adjust positions if market conditions change unexpectedly.
- Market Conditions
- Match strategies to the prevailing market trend and volatility.
- Use technical and fundamental analysis for better decision-making.
- Execution Costs
- Options trading can incur significant fees. Ensure your strategy accounts for these costs.
- Psychological Discipline
- Avoid emotional decisions. Stick to a well-defined trading plan.
Tools for Intermediate Options Traders
- Options Analysis Software: Tools like ThinkorSwim, Tastyworks, and OptionVue.
- Greeks Calculators: For precise risk management.
- Volatility Indicators: Monitor implied and historical volatility.
Conclusion
Each intermediate strategy has its unique benefits and risks. By understanding these strategies in detail and applying them with real-life market scenarios, you can enhance your options trading skills, improve profitability, and better manage risks. The key to success lies in tailoring strategies to market conditions and maintaining discipline in execution.