In today’s fast-paced world, achieving financial security and independence is a priority for many. While saving money is crucial, investing takes your financial journey a step further by enabling your wealth to grow exponentially over time. This guide will not only explain why investing matters but also provide insights into how it works, its benefits, and how you can get started.
What is Investing?

Investing is the process of allocating money into assets or ventures with the expectation of earning a profit or return. It involves putting your money to work in a variety of investment vehicles such as:
- Stocks: Shares of ownership in companies.
- Bonds: Debt securities issued by corporations or governments.
- Real Estate: Physical properties or real estate investment trusts (REITs).
- Mutual Funds and ETFs: Pooled investments in diversified portfolios.
- Cryptocurrencies: Digital currencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum.
Unlike saving, which focuses on preserving money, investing is aimed at generating returns, leveraging time, and compounding to grow wealth.
The Importance of Investing
1. Wealth Building Through Compound Interest
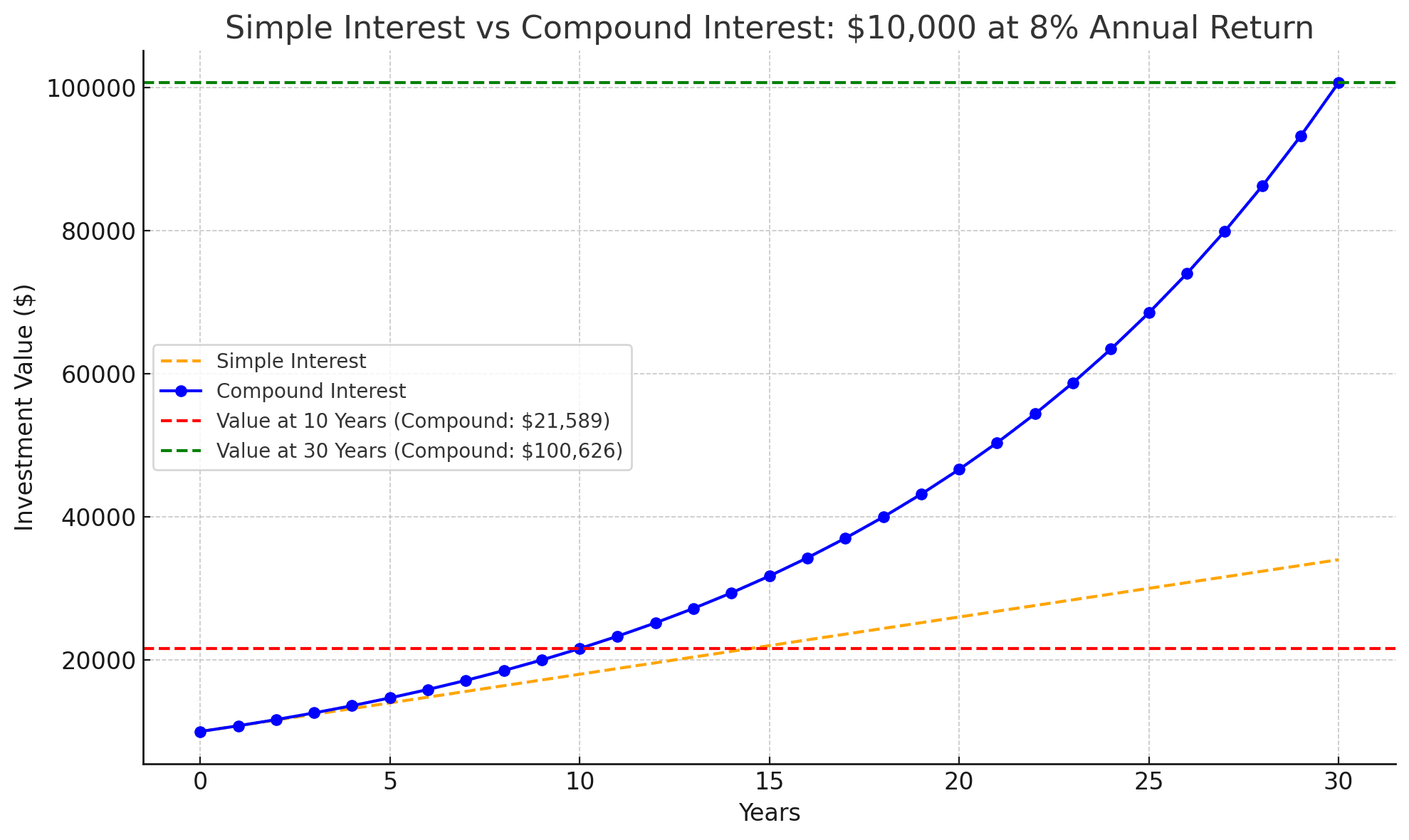
Compound interest is often called the eighth wonder of the world. It allows your investments to grow exponentially by earning interest on both the principal and previously earned interest. For example:
- Scenario: You invest $10,000 at an annual return of 8%.
- After 10 years, your investment grows to $21,589.
- After 30 years, it balloons to $100,626.
The earlier you start, the more significant the impact of compounding.
2. Protection Against Inflation
Inflation erodes the purchasing power of your money over time. For example:
- What $100 could buy 10 years ago now requires $120 or more.
Investing in inflation-beating assets such as equities and real estate ensures that your money retains its value and grows above inflation rates.
3. Achieving Financial Goals
Whether you’re saving for a home, a child’s education, or retirement, investing helps bridge the gap between your income and your goals. For instance:
- Goal: Saving $1 million for retirement in 30 years.
- By investing $500 monthly at a 7% return, you can achieve this. Without investing, you would need to save significantly more.
4. Diversification and Risk Management
Investing across different asset classes and industries reduces the risk of losing money. A diversified portfolio might include:
- High-risk, high-reward assets like stocks or crypto.
- Low-risk, steady-growth assets like bonds or real estate.
For instance, during economic downturns, bonds or gold may perform better than equities, balancing your portfolio.
5. Passive Income Generation
Investments like dividend-paying stocks, rental properties, or bonds can generate regular income without active involvement. This passive income can supplement your job earnings or fund early retirement.
6. Retirement Planning
Relying solely on pensions or government schemes may not be sufficient. Investing through retirement accounts such as 401(k)s, IRAs, or similar programs ensures financial independence in your golden years.
7. Empowering Financial Independence
Investing frees you from living paycheck to paycheck. Over time, the returns from your investments can cover living expenses, allowing you to focus on passions or pursue early retirement.
Types of Investments

1. Stocks
- Ownership in companies.
- High returns over the long term but volatile in the short term.
- Example: Investing in tech companies like Apple or Microsoft.
2. Bonds
- Fixed-income securities issued by governments or corporations.
- Safer than stocks, suitable for conservative investors.
- Example: U.S. Treasury Bonds.
3. Real Estate
- Physical property investments or REITs.
- Provides rental income and value appreciation.
- Example: Owning a rental apartment or investing in a commercial property REIT.
4. Mutual Funds and ETFs
- Pooled funds managed by professionals.
- Diversified exposure to multiple assets.
- Example: Vanguard S&P 500 ETF.
5. Cryptocurrencies
- Digital assets like Bitcoin or Ethereum.
- High-risk but potentially high-reward for tech-savvy investors.
- Example: Using Coinbase to buy Bitcoin.
6. Commodities
- Tangible assets like gold, silver, or oil.
- Serve as a hedge against inflation.
- Example: Buying gold ETFs or futures.
How to Start Investing

Step 1: Assess Your Financial Health
- Build an emergency fund (3–6 months of living expenses).
- Pay off high-interest debt, such as credit cards.
Step 2: Define Your Goals
Ask yourself:
- Are you investing for short-term goals (1–3 years) or long-term goals (10+ years)?
- What is your risk tolerance?
Step 3: Learn the Basics
- Understand terms like ROI (Return on Investment), diversification, and asset allocation.
- Use resources like Investopedia or books such as The Intelligent Investor by Benjamin Graham.
Step 4: Choose an Investment Platform
- Brokerages: Interactive Brokers, Robinhood, Fidelity, or Charles Schwab.
- Robo-advisors: Betterment or Wealthfront for beginners.
- Apps: Acorns or Stash for micro-investing.
Step 5: Start Small
- Begin with as little as $10 if needed.
- Many platforms allow fractional share purchases.
Step 6: Diversify Your Portfolio
Invest across different asset classes to minimize risk.
Step 7: Monitor and Adjust
- Regularly review your portfolio.
- Rebalance annually to maintain your desired asset allocation.
Common Myths About Investing
1. You Need a Lot of Money to Start
Fact: Platforms like Acorns or Robinhood allow investing with as little as $1.
2. Investing is Too Risky
Fact: Risk can be managed through diversification and investing for the long term.
3. You Need Expert Knowledge
Fact: Beginners can start with simple tools like index funds or robo-advisors.
FAQs About Investing
Q: What’s the best age to start investing?
A: The earlier, the better. Starting in your 20s allows you to leverage compound interest over a longer period.
Q: What’s the safest investment?
A: Government bonds or money market accounts are considered low-risk options.
Q: How do I know what to invest in?
A: Assess your goals, risk tolerance, and research options. Start with index funds for simplicity.
Conclusion
Investing isn’t just for the wealthy or financially savvy—it’s for anyone looking to build a secure future. By understanding its importance, starting early, and leveraging the right tools, you can unlock your financial potential and achieve your life goals. The best time to start investing is today. Don’t wait—take that first step toward financial independence now!