In the last article, we discussed monetary policy and briefly touched on the FOMC. In this article, let’s explore what the FOMC is, what it does, and how it impacts financial markets in detail.
What is FOMC?
FOMC means the Federal Open Market Committee. It’s a crucial part of the United States Federal Reserve System, which makes big decisions about monetary policy.
It was established by the Banking Act of 1933 and the Federal Reserve Act of 1913.
The FOMC has 12 members, including seven people from the Federal Reserve Board (the main governors’ board) and five presidents of the Federal Reserve Banks. The Chair of the Federal Reserve also leads the FOMC.
They have eight meetings every year, and everyone pays close attention to what they decide because it affects financial markets a lot.
In these meetings, they look at how the economy is doing and then decide what to do with monetary policy. This could mean changing interest rates—making them higher or lower—or thinking about ways to make more or less money available.
They do this in different ways, like controlling how much money is out there, making rules for banks, and, very importantly, lending money to banks and deciding how much interest to charge. When interest rates are low, banks borrow more money and lend it to businesses and people. But if interest rates go up, borrowing costs more, so people might not borrow as much and spend less. That gives the Fed a lot of power over how much money is around.
The Federal Reserve also sets the rules for how much money banks need to keep, and when this is less, more money moves around the economy. Also, the Fed sets the interest rates for when banks lend to each other. If these rates are low, banks borrow more from each other, which boosts the money supply. But if rates are high, banks don’t borrow as much.
And the Fed can change how much money is out there by buying or selling government bonds. When they buy bonds, they put more money into the economy, which lowers interest rates. Selling bonds takes money out, so interest rates go up. This is called quantitative easing.
When there’s more money around, prices usually go up, which is inflation. More money means more demand, so prices rise. So, the Fed has to be careful not to put too much money into the economy, or prices might go up too much.
Importance of FOMC in Trading
The money supply has a big effect on how much people spend, which really matters for the economy. And this has a flip-flop effect on stock prices and interest rates.
When interest rates go up, people are less keen to borrow money, so they spend less. Plus, folks who have cash might stash it in the bank since they can earn more interest, meaning they’re not spending it. This slowdown in spending usually means stock prices drop.
But when interest rates go down, it’s easier to get loans, so people spend more. Also, those with money in the bank might not save it as much since the interest they earn isn’t so great. This uptick in spending helps the economy and usually boosts stock prices.
So, it’s kind of like a see-saw happening here. When interest rates fall, stock prices usually go up, and when interest rates rise, stock prices often go down.
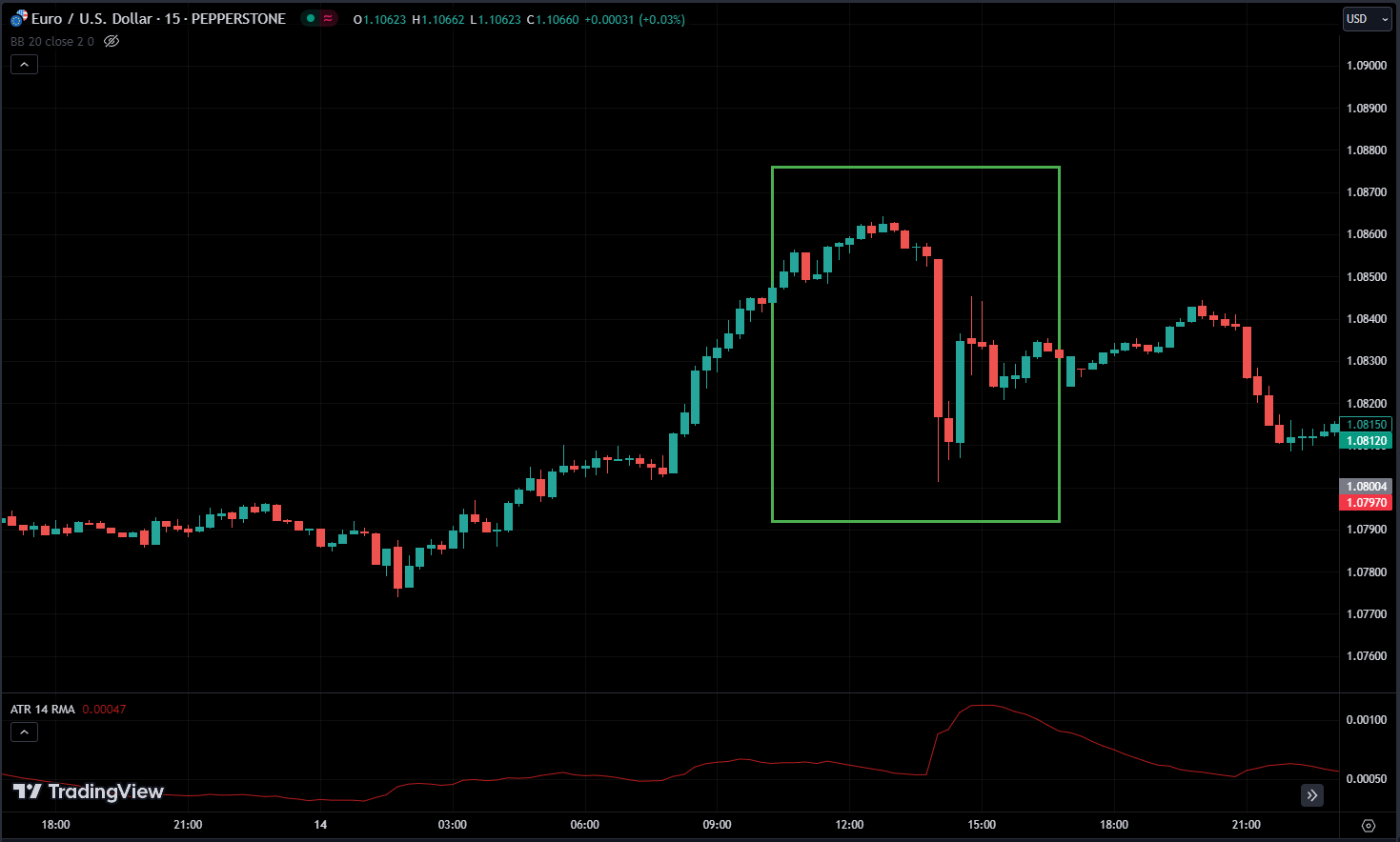
Because of this back-and-forth, it’s super important to be careful when the FOMC meets. People need to watch the market closely during those times because if everyone thinks interest rates won’t change, but then the FOMC decides to bump them up unexpectedly, stock prices might take a hit. Investors might not like the higher interest rates, so stocks lose value since they were priced based on lower rates before.
How to Watch Out for FOMC Meetings?
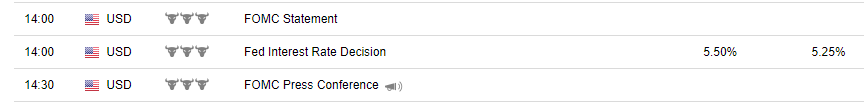
As traders, we rely on economic calendars to keep track of significant events such as FOMC meetings, which are often marked as high volatility events. It’s essential to monitor these calendars regularly as part of our daily trading routine.
Checking the calendar before each trading session is a must to stay informed about potential market-moving events.
Bloomberg and Trading Economics are examples of reliable calendars that provide valuable information for traders.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Federal Open Market Committee plays a central role in shaping the course of monetary policy in the United States. Through its careful analysis of economic data and deliberative policymaking process, the FOMC seeks to achieve its dual mandate of price stability and maximum employment.
The decisions of the FOMC have far-reaching implications for financial markets, influencing interest rates, asset prices, and exchange rates both domestically and internationally. As such, understanding the functions and impact of the FOMC is essential for investors, policymakers, and anyone with an interest in the workings of the global economy.