Compound interest is a fundamental concept in the world of investing, often referred to as the “eighth wonder of the world” by those who understand its power. It’s a powerful tool that can significantly enhance the growth of your investments over time. In this article, we’ll explore what compound interest is, how it works, and why it is essential for investors.
What is Compound Interest?
Compound interest is the interest on a loan or deposit calculated based on both the initial principal and the accumulated interest from previous periods. Unlike simple interest, which is only calculated on the principal amount, compound interest grows exponentially because interest is earned on both the principal and the previously accumulated interest.
Compounding occurs when you invest your money and, instead of withdrawing the interest you earn, you reinvest it. By doing so, you not only earn interest on your initial investment but also on the interest generated in previous periods. This powerful process multiplies your returns over time.
The longer you leave your money invested, the more time it has to benefit from compound interest. Compound interest tends to have a more significant impact over extended periods.
Investments can compound at different intervals, such as annually, semi-annually, quarterly, or even daily. The more frequent the compounding, the faster your wealth can grow.
Compound interest is a compelling reason to start investing early and to remain invested for the long term. It rewards patience and consistent contributions to your investment portfolio. It is a key factor in building wealth and achieving financial goals over time.
The Formula for Compound Interest

Example:
Consider having $10,000, and your intention is to invest it and let it grow over a span of 20 years. Assuming you earn a 10% interest rate annually, and you withdraw the interest every year. In this scenario, you would receive $1,000 each year. So, how much would you have accumulated by the end of the 20-year period? You’d start with your initial $10,000 and add the $1,000 earned each year for 20 years, resulting in a total of $30,000.
Now, let’s consider the same scenario but with compounding in play. Here’s how it works: After you earn your initial interest of $1,000, you reinvest that money along with your initial $10,000, resulting in a new deposit of $11,000. Consequently, the interest you earn in the next period will be 10% of $11,000, which equals $1,100.
So, in the next period, your total will be $11,000 + $1,100, totaling $12,100, and the interest for that period will be 10% of $12,100, which amounts to $1,210.
You repeat this process for all 20 years, and by the end of that period, you will have accumulated $67,275.
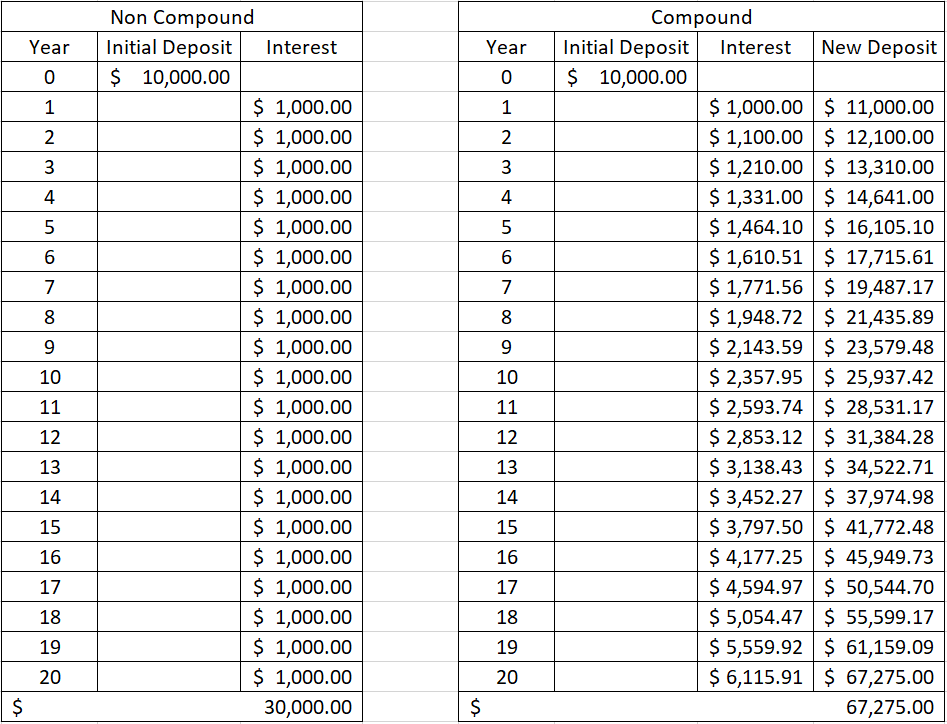
Each year, you’ll notice that the interest you earn isn’t stagnant; it grows, and this growth is due to the compounding effect. It accelerates so rapidly that after 20 years, instead of merely earning $1,000 on your initial investment, you’ll be earning $6,115 and so on it goes. The remarkable thing is, you didn’t have to put in any extra effort; you simply let that interest accumulate and grow. Without compounding, you’d only end up with $30,000, but with compounding, your total would reach $67,275.
There are many online compound interest rate calculators for you to choose, and the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) also provides its own version.
The Power of Time
One of the most critical factors in leveraging compound interest is time. The longer you allow your money to compound, the greater the growth of your investment. This principle highlights the importance of starting to invest early. Even small investments can grow significantly over a long period due to the effect of compounding.
Long-Term Growth Example
Consider two investors: Investor A and Investor B. Investor A starts investing $5,000 per year at the age of 25 and stops after 10 years, having invested a total of $50,000. Investor B starts investing $5,000 per year at the age of 35 and continues until the age of 65, investing a total of $150,000. Assuming an annual interest rate of 7%, compounded annually:
- Investor A:
- Total investment: $50,000
- Future value at age 65: Approximately $602,070
- Investor B:
- Total investment: $150,000
- Future value at age 65: Approximately $540,741
Despite investing less money, Investor A ends up with more due to the power of starting early and allowing compound interest to work over a longer period.
Why Compound Interest is Essential for Investors?
Wealth Accumulation: Compound interest is a crucial mechanism for wealth accumulation. It allows your investments to grow more quickly than they would with simple interest. Over time, the growth of your investment can accelerate, turning modest savings into substantial wealth.
Inflation Protection: Inflation erodes the purchasing power of money over time. To combat inflation, investments need to grow at a rate that outpaces the inflation rate. Compound interest can help achieve this by providing higher returns, ensuring that your investment retains its purchasing power in the future.
Retirement Planning: For retirement planning, compound interest is particularly important. Starting to save and invest early for retirement allows compound interest to work its magic, providing a larger retirement nest egg. Even small, regular contributions can grow significantly over a working lifetime.
Conclusion
Understanding and harnessing the power of compound interest is essential for successful investing. By starting early, investing consistently, and choosing investments that compound frequently, you can maximize the growth of your wealth. Whether you’re saving for retirement, a major purchase, or simply building your financial security, compound interest can help you achieve your financial goals more effectively.