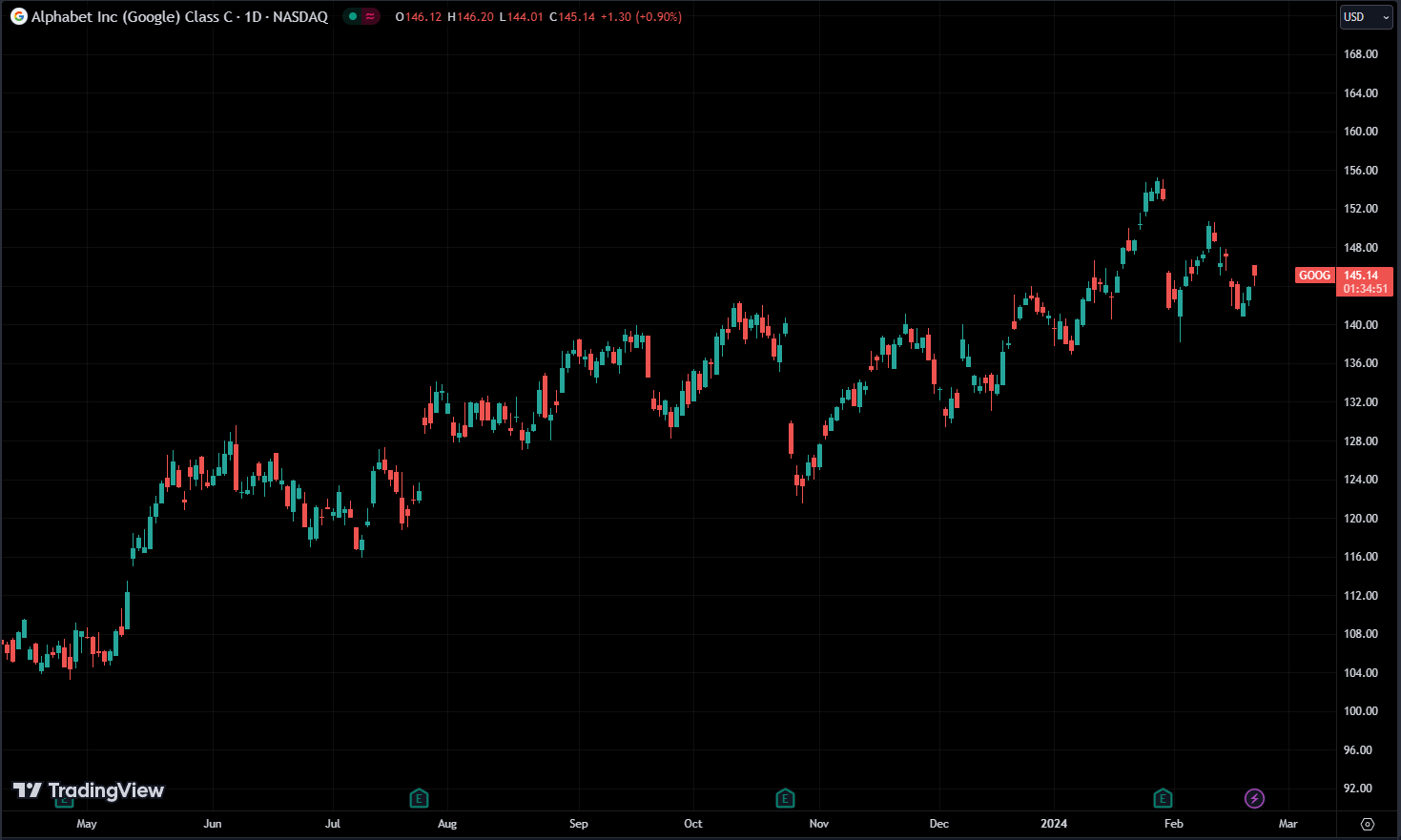
Sometimes when you look at a stock price chart, you’ll notice gaps between the daily bars. This happens when the stock starts trading at a price that’s higher or lower than where it closed the day before.
Why does this happen? there must be a reason why stocks open at different price levels. so how opening price of a stock is decided? Well, It’s decided by something called Opening Auction.
What is the Opening Auction?
Every morning, there’s an auction we call the “opening auction.” It’s run by the exchange and decides the starting price for stocks. This process helps them figure out where to set the initial stock price for the day.
To take part in this auction, you can do so by sending two types of orders:
- Limit On Open (LOO)
- Market On Open (MOO)
And what the exchange basically does is take all these orders and try to determine the best price at which to open the stock, filling the orders of most participants in this auction.
Example:
Let’s simplify it. Imagine yesterday a stock closed at $10. But today, before the market opens, we don’t know what price it will start at. Many people think the first trade after the market opens sets the stock’s starting price. If you’re trading on exchanges like NYSE or NASDAQ, the market opens at 9:30 AM. But that’s not exactly how it works. In reality, there’s an auction, and the exchange announces the price at 9:30 AM.
Here’s how it goes: they invite everyone to send their orders for the auction. They receive buy orders and sell orders. For example, let’s say two buy orders come in: one for 100 shares at $14 and another for 200 shares at $12. Then there’s a sell order for 100 shares at $13. The exchange looks at these orders and decides the opening price. They might match the buyer at $14 with the seller at $13 and set the opening price at $13.50. So, at exactly 9:30 AM, 100 shares are traded at $13.50, and that’s the opening price.
Now, usually it’s not just two orders; there are thousands of orders, and many people take part in the opening auction. Not all brokers allow you to send these orders, but a lot of brokers do. So, let’s say in this case there’s another seller with a Market On Open (MOO) order for 200 shares. There’s no price specified because it’s a market order. In this scenario, what do you think the opening price would be?
Firstly, they look at the Market On Open (MOO) orders. They consider all the buy MOO and sell MOO orders and match them with each other. Then, if there are any MOO orders left over, like in our example, where there are still MOO orders from sellers, they match them with the limit on open orders from buyers. So, they might think, “Okay, this guy still wants to sell 200 shares at whatever the opening price is. He doesn’t care. Let’s see what we can give him.” They may decide to give 100 shares to the guy willing to buy at $14, and they can give another 100 shares to the guy who wants at $12.
So, they set the opening price at $12. Now, what price will the first buy order at $14 be filled at? Well, the person sent a limit on open (LOO) order. They won’t necessarily get it at $14 because there’s only one price, and everyone participating in the auction gets filled at that same price. Even though they said they wanted it at $14, they’re willing to accept anything up to $14. So, if they can get it for $12, they’ll take it. The other buyer wants to buy at $12, so they get filled. The sell MOO order also gets filled, but the sell LOO order at $13 will be canceled because the stock opens at $12, and they wanted to sell at $13.
I hope you understand how the price is actually decided. Basically, they take all the MOO orders and match them together. Anything leftover, they start matching it with LOO orders. Then, they look at all the LOO orders and determine what price they can open the stock at to fill most of these LOO orders. So, what they want is to fill the biggest quantity of orders.
Now, various exchanges have different procedures for handling these orders. For instance, some exchanges like NASDAQ & NYSE require you to send all orders before 9:28 AM. You can find more information about them on their websites.
What is the Closing Auction?
Just like how the opening price is determined, the closing price of a stock is also decided through an auction, known as the Closing auction.
To take part in this auction, you can do so by sending these orders:
- Limit On Close (LOC)
- Market On Close (MOC)
Importance of Opening and Closing Prices
These prices are crucial because they establish the starting and ending points for a day’s trading activity. Traders often analyze these prices to gauge market sentiment and determine potential trading opportunities.
The opening price can indicate how investors are reacting to news or events overnight, setting the tone for the trading day. Similarly, the closing price reflects the final consensus among investors before the market closes.
Traders may use opening and closing prices as reference points for setting entry and exit points for their trades. Understanding these prices can help traders formulate more effective trading strategies. one famous strategy is known as OPG (Open Gap).
Impact of Auctions on Trading Strategies
Traders leverage knowledge of opening and closing auctions to optimize their trading strategies. For example, they may identify discrepancies between auction prices and market expectations to execute profitable trades.
Utilizing auction orders such as LOO and MOO, traders can enter or exit positions at advantageous prices during the opening and closing auctions.
By incorporating auction dynamics into their strategies, traders can capitalize on market inefficiencies and maximize their trading opportunities.
Market Volatility and Auctions
Market volatility can affect the auction process by influencing order flow and price discovery. During periods of heightened volatility, opening and closing prices may exhibit greater variability.
Understanding how volatility impacts auction dynamics enables traders to anticipate price movements and adjust their strategies to mitigate risks and seize opportunities.
Regulatory Considerations
Regulatory requirements ensure fairness and transparency in the auction process. Exchanges enforce rules governing order submission times, order types, and trade execution procedures to maintain market integrity.
Compliance with regulatory standards fosters investor confidence and promotes orderly trading behavior. Traders must adhere to these regulations to ensure their participation in auctions is in accordance with exchange rules.
Regulatory oversight helps maintain market stability and prevents market manipulation, safeguarding the interests of investors and market participants.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding how stock prices are determined is crucial for traders. The opening and closing prices of stocks are determined through auctions conducted by exchanges like NASDAQ and NYSE. During the opening auction, orders such as Limit On Open (LOO) and Market On Open (MOO) are matched to set the initial price for trading. Similarly, the closing price is determined through a similar auction process, known as the Closing auction, where orders like Limit On Close (LOC) and Market On Close (MOC) are utilized.
These auctions ensure fairness and transparency in setting stock prices, allowing traders to make informed decisions. It’s essential to note that different exchanges have varying procedures for submitting orders, emphasizing the need for investors to familiarize themselves with the rules of the exchange they trade on.
By understanding these processes, traders can navigate the stock market more effectively and capitalize on opportunities for profitable trading.