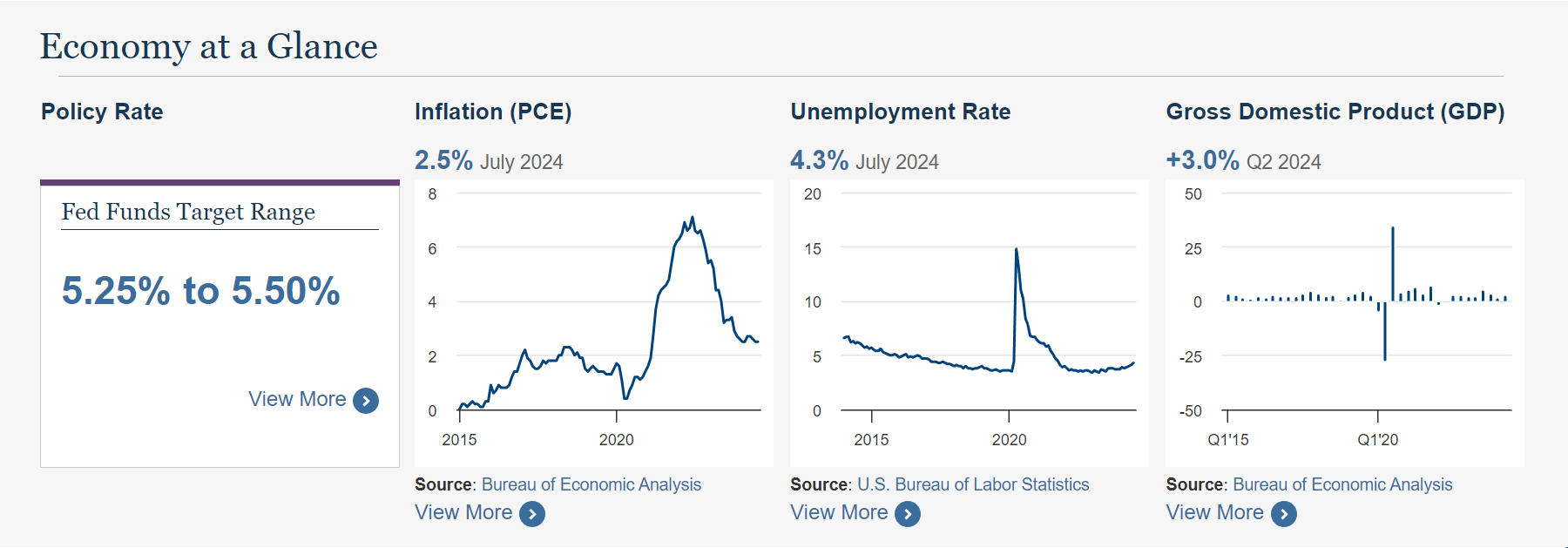
As the economic landscape in the U.S. remains highly sensitive to inflationary pressures and growth signals, all eyes are on the upcoming August jobs report. This key report is expected to significantly influence the Federal Reserve’s decision on whether to adjust interest rates in their forthcoming meetings. Over the past several months, the Fed has been navigating a delicate path, attempting to tame persistent inflation without triggering a recession, while ensuring that the labor market remains resilient. The August jobs report may hold the answers to their next steps.
Understanding the Importance of the August Jobs Report
The August report will provide crucial insights into the state of the labor market. Key metrics such as nonfarm payroll growth, unemployment rate, and wage inflation will be closely monitored by both Federal Reserve officials and market participants. A strong showing in the report, reflected in high job creation and rising wages, could indicate that the economy is still running hotter than desired, necessitating a more restrained approach from the Fed. In contrast, signs of softening, such as slowing job growth or higher unemployment, could open the door for a more aggressive rate cut aimed at stimulating economic activity.
At the heart of this debate lies the Fed’s dual mandate: promoting maximum employment while maintaining price stability. If inflationary pressures persist but the labor market remains tight, the Fed may opt for a smaller rate cut or even decide to pause further cuts to prevent overheating. However, should the report reveal a weakening labor market, the Fed could feel compelled to lower interest rates more significantly to prevent a broader economic slowdown.
Labor Market Trends and Economic Signals
Several factors will be taken into account as the Fed analyzes the data. One of the most important indicators is wage growth, which has been a significant driver of inflation. If wages continue to rise, it could exacerbate inflationary pressures, forcing the Fed to act cautiously. Additionally, the unemployment rate will be closely scrutinized. A decrease in unemployment could suggest that the labor market remains strong, while an increase could signal that economic headwinds are beginning to take a toll.
Other data, such as the labor force participation rate, will also offer clues about the health of the job market. Higher participation may indicate that more people are entering the workforce, while lower participation could be a sign of weakening confidence in the economy. These factors combined will offer the Federal Reserve a more comprehensive view of where the economy stands and help them decide whether to take a more aggressive or conservative approach in future rate decisions.
Market Reactions and Investor Sentiment
Investors and traders are keenly aware of the stakes involved in the August jobs report. Financial markets are particularly sensitive to any changes in the Federal Reserve’s policy stance, with equity markets, bond yields, and even foreign exchange rates likely to react swiftly to the data. A strong jobs report, signaling less need for stimulus, could cause bond yields to rise and equity markets to cool as the prospect of lower interest rates fades. Conversely, weaker data could bolster expectations of deeper cuts, leading to a rally in both stocks and bonds.
Historically, the Fed has responded quickly to labor market shocks, with rate cuts often following significant downturns in employment data. Given the persistent uncertainty surrounding inflation and global economic headwinds, this report is seen as a key factor that could either reaffirm or upend current market expectations for a rate cut in the next Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) meeting.
Potential Outcomes for the Federal Reserve’s Policy
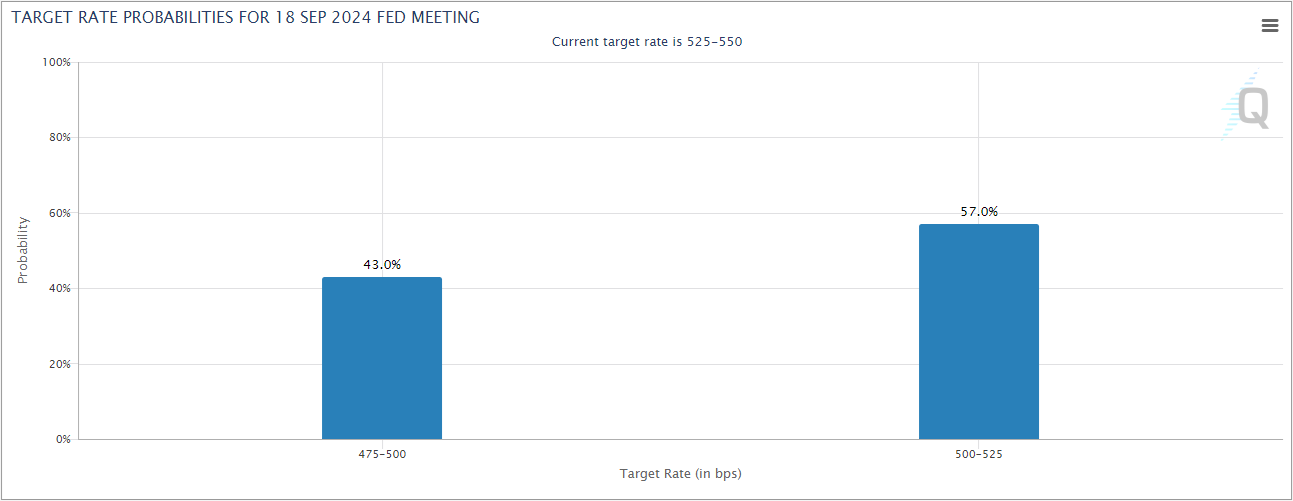
Several scenarios are possible depending on the outcome of the report. A stronger-than-expected labor market could prompt the Fed to scale back its plans for a rate cut, potentially opting for a more modest reduction or delaying further cuts altogether. This would indicate that the economy is still growing at a healthy pace, reducing the immediate need for further monetary easing. However, a weaker report, with signs of job losses or stagnating wage growth, might push the Fed to implement a more substantial cut, perhaps even higher than the 0.25% cut that many analysts currently expect.
It’s also worth noting that the Fed has multiple considerations beyond just employment data. Global economic risks, trade tensions, and inflationary pressures will also weigh heavily on their decision-making process. But the August jobs report, given its role as a primary indicator of the health of the U.S. economy, remains a critical piece of the puzzle. Policymakers will likely be very cautious, ensuring they have enough data to make informed decisions about the trajectory of interest rates.
Conclusion
As we approach the release of the August jobs report, anticipation is building across financial markets and within the Federal Reserve itself. The data could confirm that the economy is strong enough to weather additional rate cuts or signal that deeper cuts are necessary to prevent a slowdown. Regardless of the outcome, this report will be a critical factor in determining the Fed’s policy in the coming months. Investors, economists, and policymakers will be paying close attention to every detail, knowing that the future of monetary policy hangs in the balance.
