Trading in the financial markets offers exciting opportunities to grow your wealth, but it also comes with inherent risks. One of the most crucial tools traders use to manage these risks is a stop loss order. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced trader, understanding stop-loss orders is essential for effective risk management and long-term success in trading.
What Is a Stop Loss Order?
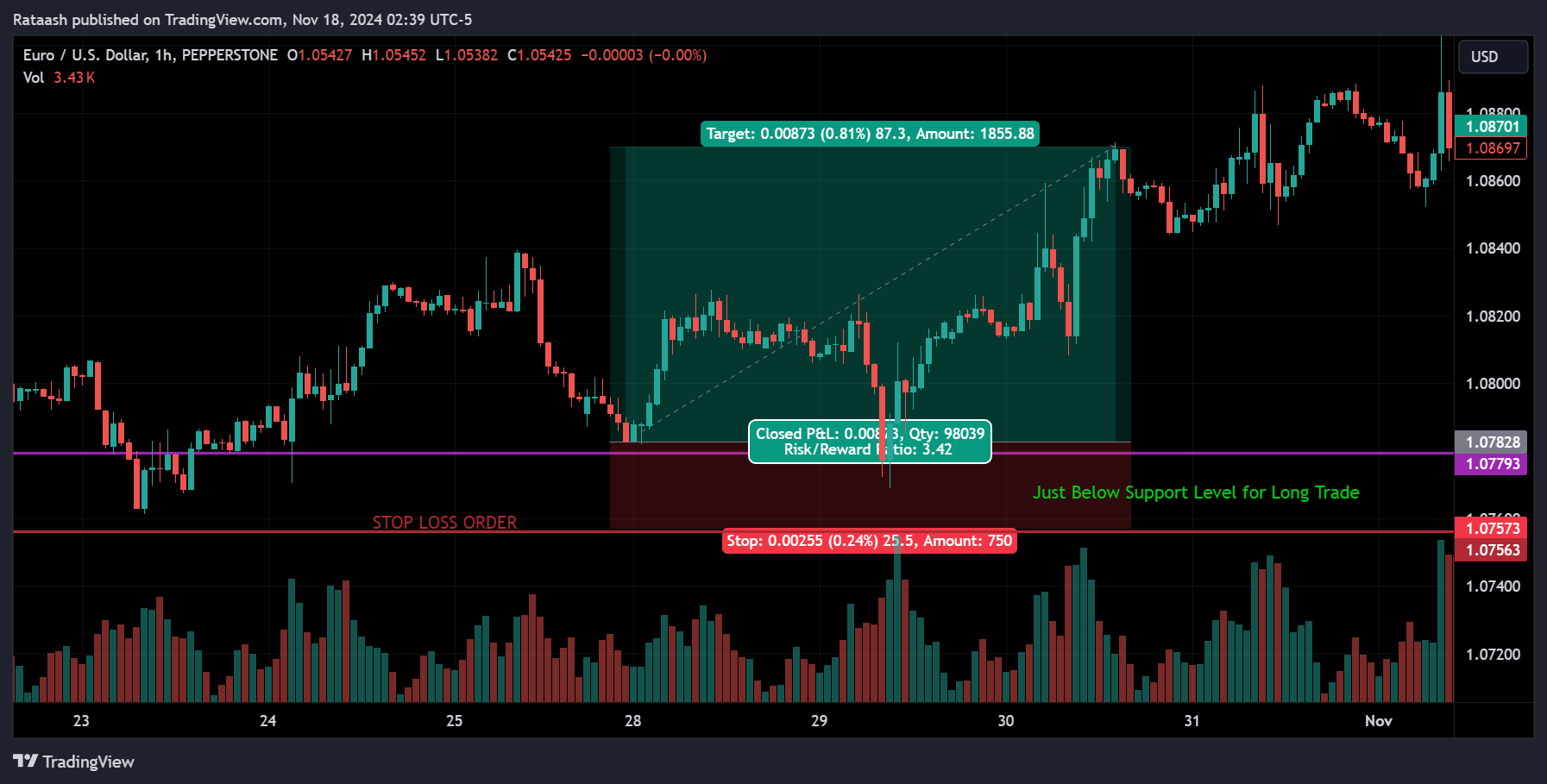
A stop loss order is a pre-defined instruction to your broker to sell a security when it reaches a certain price. The primary purpose of a stop loss order is to limit potential losses in a trade by automatically exiting the position when the price moves against you.
How Does a Stop Loss Work?
When you place a stop loss order, you set a specific price level at which the order will be triggered. If the market price reaches or falls below this level, the stop-loss order converts into a market order, and your position is sold at the best available price.
For example:
- If you buy a stock at $100 and set a stop loss at $95, the order will execute automatically if the stock price drops to $95 or lower, minimizing your loss to $5 per share.
Importance of Stop Loss in Trading
1. Limits Losses
The primary advantage of using a stop loss order is that it protects your trading capital. By pre-defining the amount you’re willing to lose, you can trade with peace of mind, knowing your losses are controlled.
2. Reduces Emotional Trading
Market volatility can lead to emotional decision-making, which often results in poor trading choices. A stop loss order removes emotions from the equation by automating the exit strategy.
3. Helps in Risk-Reward Analysis
A stop loss is an integral part of the risk-reward ratio calculation. By knowing the potential loss (stop-loss level) and potential profit (target price), traders can decide whether a trade is worth taking.
4. Prevents Overexposure
Without a stop-loss, traders might hold onto losing positions, hoping for a reversal, which can lead to significant losses. A stop loss ensures that your capital is preserved for better trading opportunities.
5. Encourages Discipline
Using a stop loss promotes disciplined trading habits by enforcing risk management strategies consistently.
Types of Stop-Loss Orders
There are several types of stop-loss orders that traders can use based on their strategies and the market conditions:
1. Fixed Stop-Loss
A fixed stop-loss is placed at a specific price level based on your analysis. It does not change once set.
2. Trailing Stop-Loss
A trailing stop-loss adjusts as the price moves in your favor. It helps lock in profits while still protecting against significant losses.
For example:
- If you set a trailing stop of $5 and the price moves from $100 to $110, the stop-loss will adjust to $105. If the price drops to $105, the position will be sold, securing a profit of $5.
3. Percentage Stop-Loss
This stop-loss is set at a percentage below the entry price. For example, if you buy a stock at $100 and set a 5% stop-loss, the order will trigger if the price falls to $95.
4. Volatility-Based Stop-Loss
This method uses market volatility to determine the stop-loss level. For highly volatile assets, the stop-loss is set further away from the entry price to avoid being stopped out prematurely.
How to Set an Effective Stop-Loss
1. Identify Key Support and Resistance Levels
Setting your stop-loss below a strong support level (for long positions) or above a resistance level (for short positions) can reduce the chances of being stopped out during normal market fluctuations.
2. Consider Your Risk Tolerance
Assess how much of your trading capital you’re willing to lose on a single trade. A common rule is to risk no more than 1-2% of your total capital per trade.
3. Align with Your Trading Strategy
Different strategies require different stop-loss placements. For example, day traders may use tighter stop-losses compared to swing traders, who might allow for more price movement.
4. Monitor Market Conditions
Adapting your stop-loss strategy to current market conditions, such as volatility and liquidity, can improve its effectiveness.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Using Stop-Loss Orders
- Placing Stop-Loss Too Close Setting the stop-loss too close to your entry point can lead to premature exits, especially in volatile markets.
- Failing to Adjust Stop-Loss Not updating your stop-loss based on price movement or new information can lead to missed opportunities to lock in profits.
- Ignoring Market Events Major news events can cause sudden price spikes or gaps. Be aware of such events when placing stop-loss orders.
- Over-Reliance on Stop-Loss While a stop-loss is an excellent risk management tool, it should not replace thorough market analysis and a well-thought-out trading plan.
Conclusion
A stop-loss order is a powerful risk management tool that every trader should understand and implement. By limiting potential losses, reducing emotional trading, and encouraging discipline, stop-loss orders help traders protect their capital and stay in the game for the long term.
Whether you’re trading stocks, forex, or cryptocurrencies, incorporating stop-loss strategies into your trading plan is a step toward more consistent and profitable trading. Remember, the key to success in trading is not just about making profits—it’s about managing risks effectively.
FAQs
- Is stop-loss suitable for all types of trading? Yes, stop-loss orders are versatile and can be used in day trading, swing trading, and even long-term investing.
- Can stop-loss orders guarantee no losses? No, stop-loss orders minimize losses but cannot eliminate them entirely, especially during market gaps.
- Should I always use a stop-loss? While it’s highly recommended to use stop-loss orders, experienced traders sometimes choose not to, depending on their risk management strategies.
By understanding and applying stop-loss orders effectively, you’ll be better equipped to navigate the unpredictable waters of trading and achieve your financial goals.