Achieving consistent profitability in stock trading isn’t about luck; it’s about following a well-structured plan. This roadmap to becoming a profitable stock trader will take you through the essentials—from understanding the stock market basics to mastering advanced strategies and techniques. Whether you’re a beginner or seeking to enhance your skills, this comprehensive guide offers actionable steps to help you succeed.
1. Understanding the Basics of Stock Markets
The first step in your trading journey is understanding how the market works. Without a clear grasp of the basics, you’re more likely to make costly mistakes. Let’s break it down:
What is the Stock Market?

The stock market is a platform where shares of publicly traded companies are bought and sold. Major exchanges like the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) and NASDAQ facilitate these trades.
Understanding the market means knowing that it operates as a meeting point for buyers and sellers, and prices are determined by supply and demand.
Assets You Can Trade:
Stocks are just one type of asset. Others include ETFs, bonds, options, and derivatives.
Stocks: Shares in individual companies.
ETFs (Exchange-Traded Funds): Baskets of stocks that track specific indices or sectors.
Options: Contracts giving you the right to buy or sell a stock at a set price.
Role of Brokers:
To access the market, you’ll need a broker. Brokers act as intermediaries, executing your trades on exchanges.
Look for features like low commissions, a user-friendly platform, educational resources, and real-time data.
Action Step: Research brokers such as Interactive Brokers or Charles Schwab, and open a demo account to get hands-on experience.
2. Learn How to Buy and Sell Stocks
Once you understand the market, it’s time to learn the mechanics of trading. Knowing how to execute trades is crucial to avoid mistakes.
Order Types:
- Market Orders: Buy or sell immediately at the current price.
- Limit Orders: Set a specific price at which to buy or sell.
- Stop Orders: Trigger a buy or sell when the price reaches a certain level.
- Stop-Limit Orders: Combines stop and limit orders for more control.
Stock Quotes:
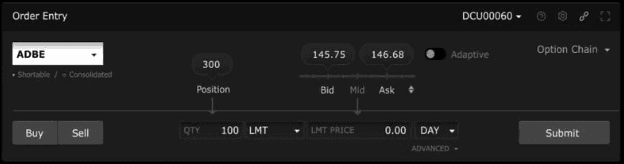
Learn to read quotes showing the stock’s current price, bid price (what buyers are willing to pay), ask price (what sellers want), and trading volume. These give insights into liquidity and market interest.
Using Trading Platforms:
Familiarize yourself with platforms like TradingView or your broker’s proprietary software. Practice navigating their features, setting up watchlists, and executing demo trades.
Pro Tip: Start small. Begin with fractional shares or small position sizes to minimize risk while learning.
3. Understand How Stock Prices Change
At the heart of profitable trading is understanding why stock prices move. Prices fluctuate due to a variety of factors, including:
Supply and Demand:
The most fundamental driver. When more people want to buy (demand) than sell (supply), the price rises. When sellers outnumber buyers, the price falls.
Market Sentiment:
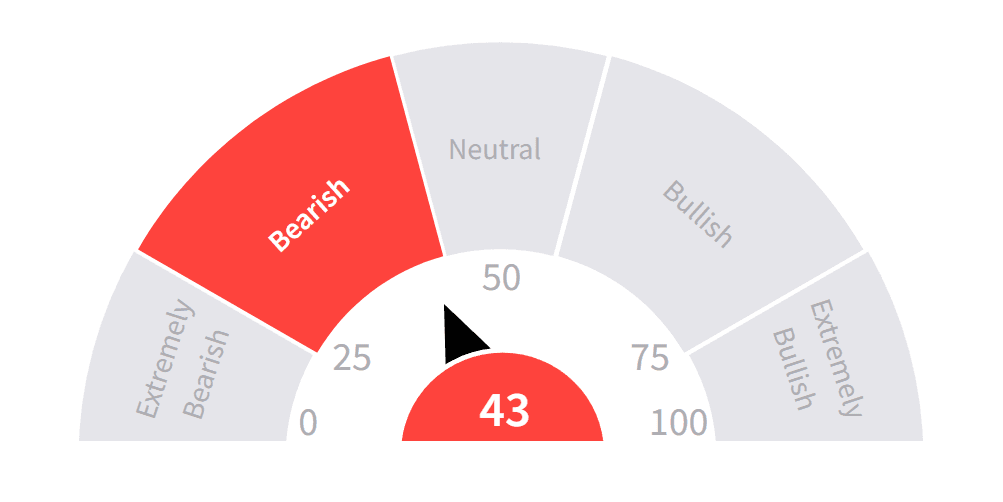
Investor emotions, influenced by news, economic events, and global trends, can create bullish (positive) or bearish (negative) markets.
Market sentiment is often displayed on trading platforms and various online websites. One of my favorite websites for gauging this sentiment is Stocktwits.
Fundamentals of the Company:
A company’s financial health, revenue, and profitability impact its stock price. For example, strong earnings reports can lead to price increases.
Macroeconomic Factors:
Interest rates, inflation, and unemployment data can shift market dynamics. For instance, rising interest rates often hurt high-growth tech stocks.
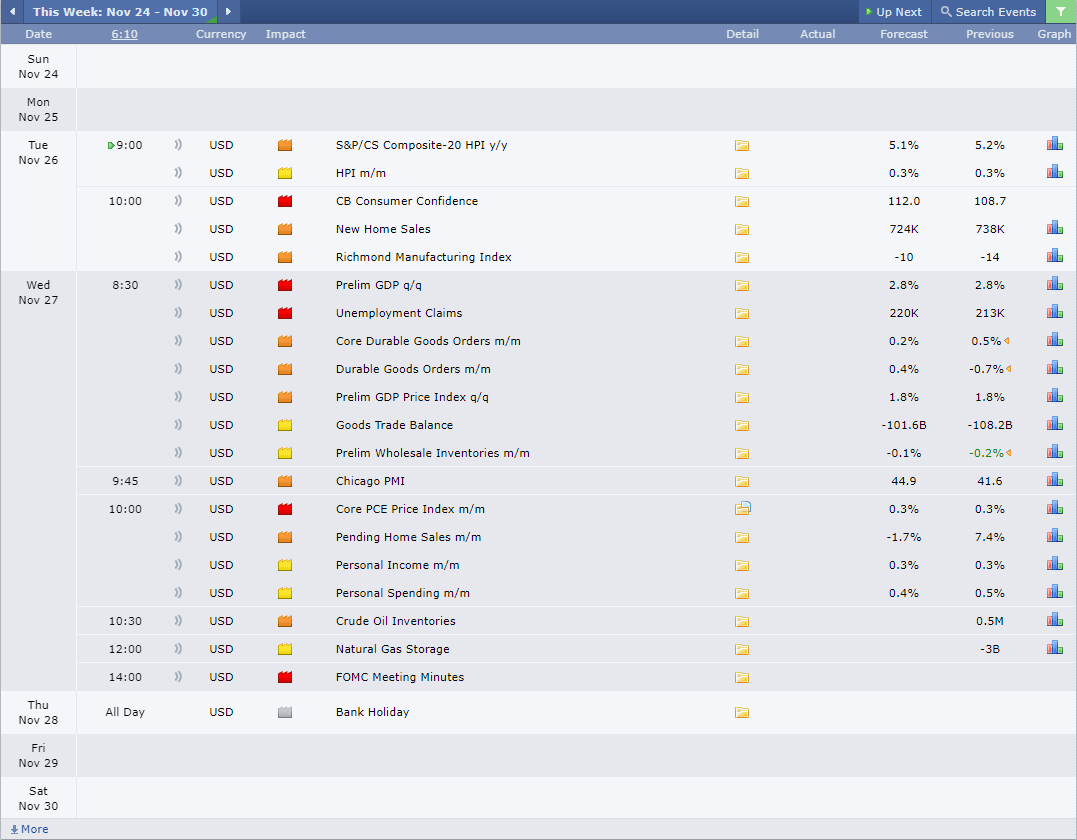
Observing macroeconomic trends is made easier with tools like economic calendars, which highlight important events and their potential impact on the markets. Websites like ForexFactory and TradingView are great resources to stay on top of these developments, providing timely updates on key events and data releases.
Action Step: Spend time observing stock charts and news to understand how events affect price movements.
4. Dive into Price Action and Supply-Demand Analysis
To excel at trading, you must read and interpret price movements directly on the chart. This is known as price action analysis.
Candlestick Patterns:
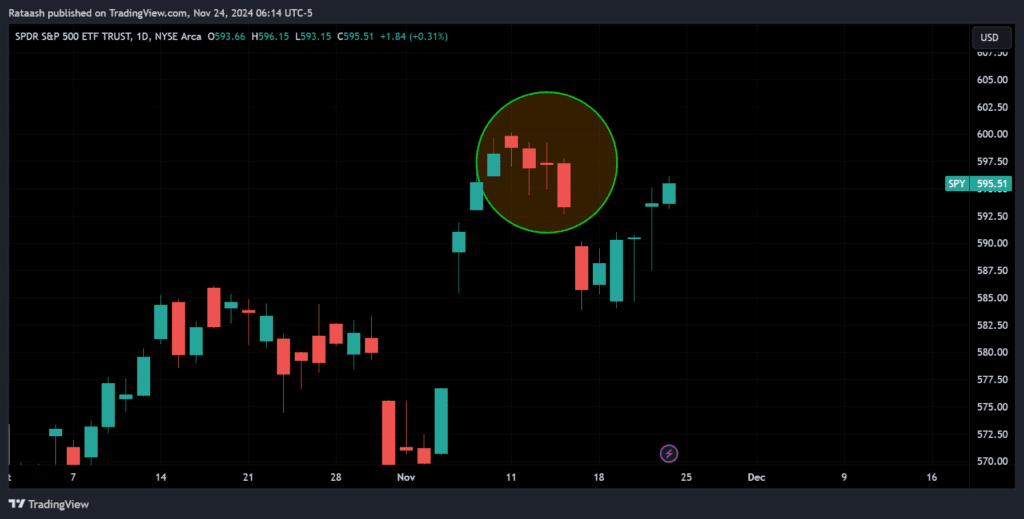
Study patterns like hammer, doji, and engulfing candles to spot potential reversals or continuations.
Support and Resistance Levels:
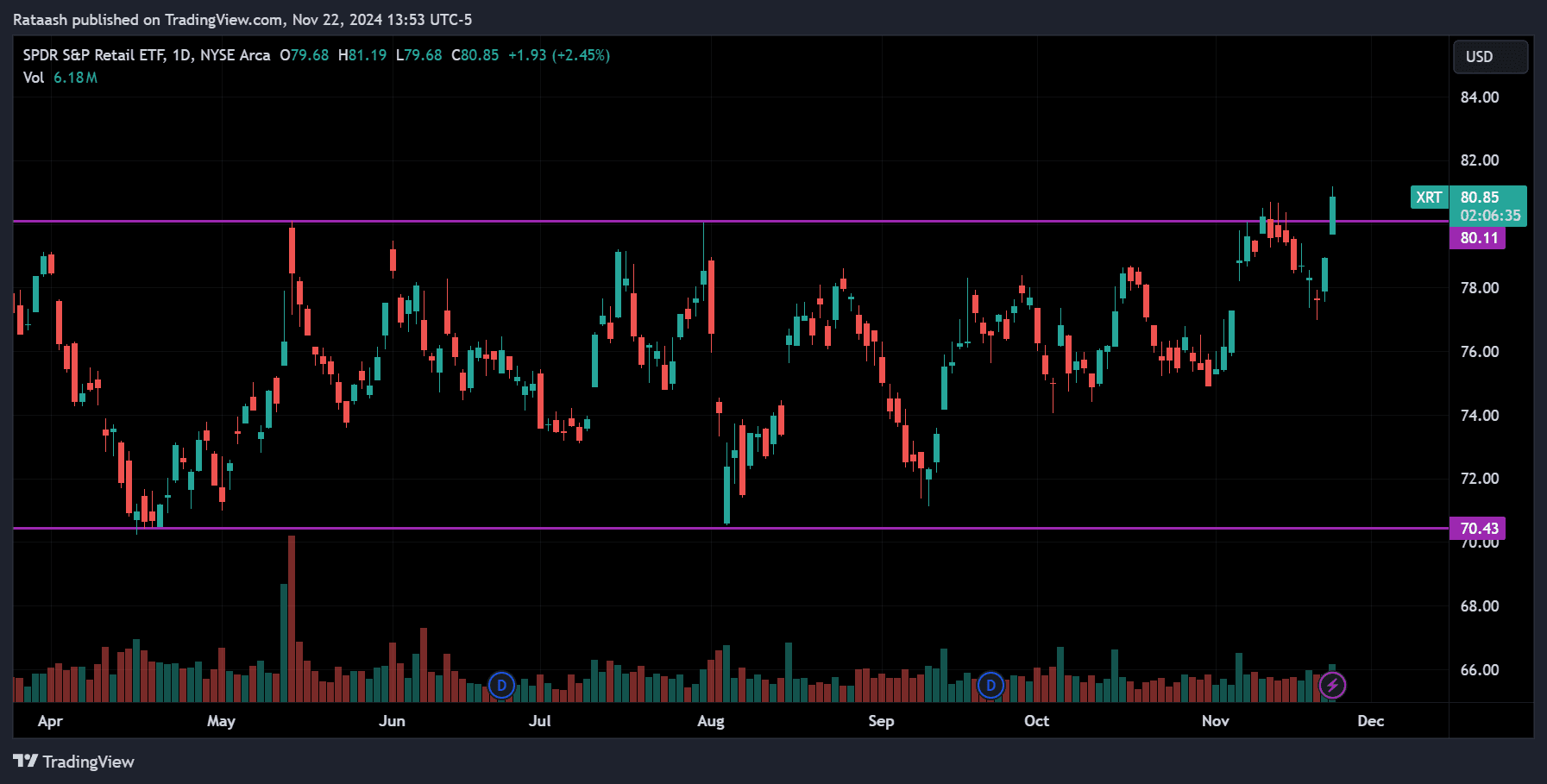
Identify price levels where stocks frequently reverse (support) or face difficulty breaking through (resistance). These levels are critical for planning entries and exits.
Supply and Demand Zones:
These are broader areas where buying or selling pressure dominates. Learning to recognize these zones helps you trade in alignment with major market forces. Most of the time, they coincide with the support and resistance levels we discussed earlier.
Pro Tip: Combine price action analysis with other tools like volume to confirm trends.
5. Study Technical Analysis
Technical analysis is the cornerstone of short-term trading. It involves analyzing past price data to predict future movements. Master these concepts:
Trend Identification:
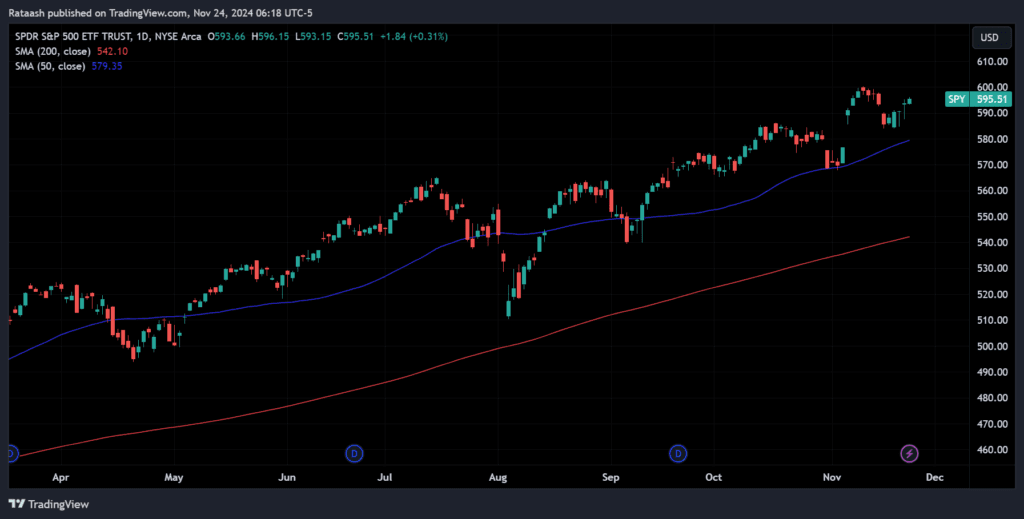
Use moving averages or trendlines to determine whether a stock is in an uptrend, downtrend, or sideways trend.
Indicators and Oscillators:
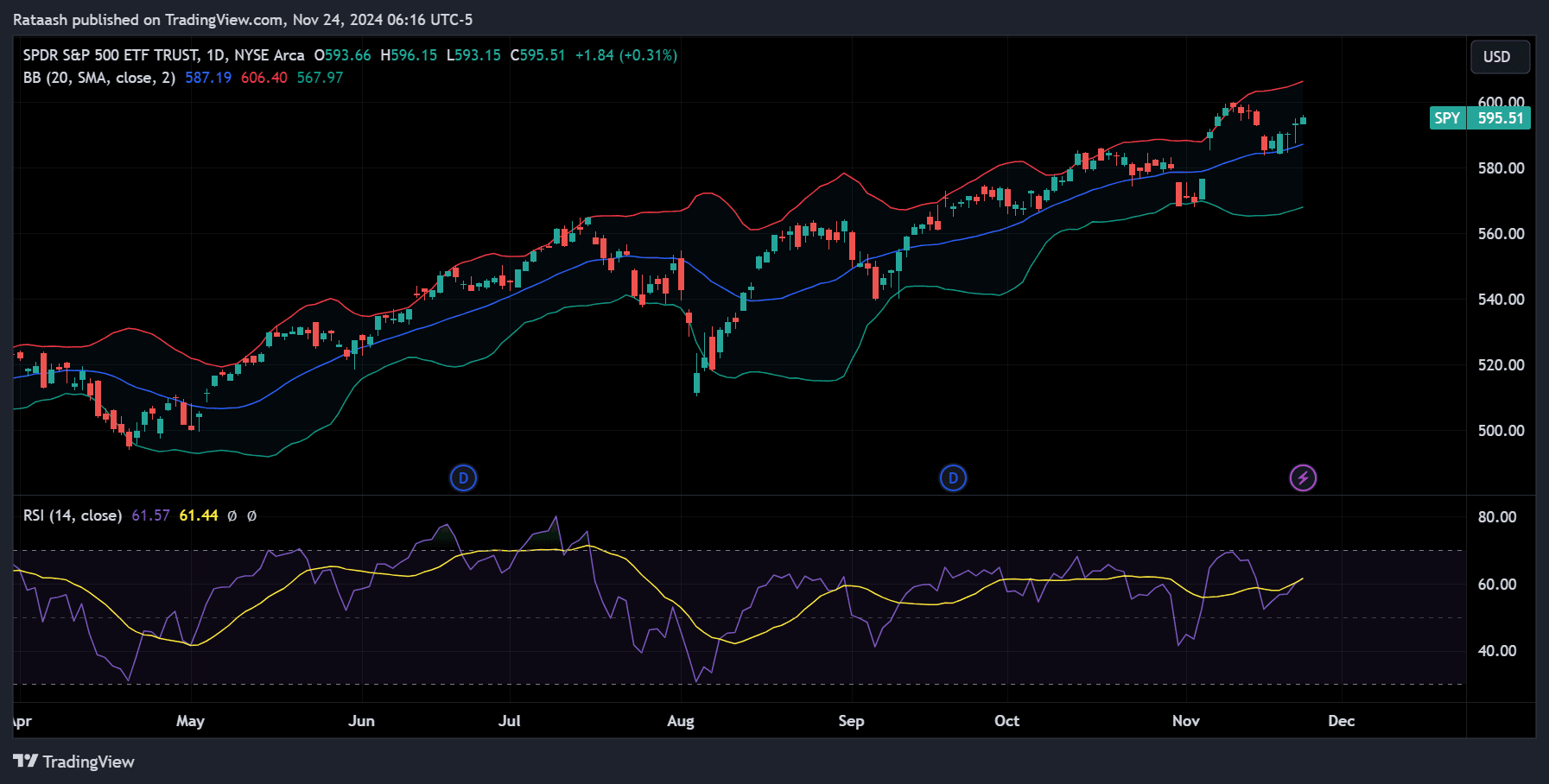
- RSI (Relative Strength Index): Measures overbought or oversold conditions.
- MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence): Identifies momentum shifts.
- Bollinger Bands: Shows volatility and potential breakout points.
Action Step: Spend time practicing technical analysis on historical charts using tools like TradingView.
6. Learn Fundamental Analysis
Long-term profitability also requires understanding the intrinsic value of a stock. Fundamental analysis focuses on:
Financial Statements:
- Income statement (revenue and profits).
- Balance sheet (assets and liabilities).
- Cash flow statement (operating, investing, and financing cash flows).
Key Ratios:
- P/E Ratio: Price-to-earnings ratio shows how a stock is valued relative to its earnings.
- Debt-to-Equity Ratio: Indicates financial stability.
Industry and Economic Trends:
Understand how broader market conditions and industry developments affect a company.
Pro Tip: Use websites like Yahoo Finance, Bloomberg, and Morningstar to gather financial data.
7. Master Risk Management
No trading strategy is complete without proper risk management. This is the difference between successful traders and those who burn through their accounts.
Position Sizing:
Never risk more than 1-2% of your trading capital on a single trade.
Stop-Loss Orders:
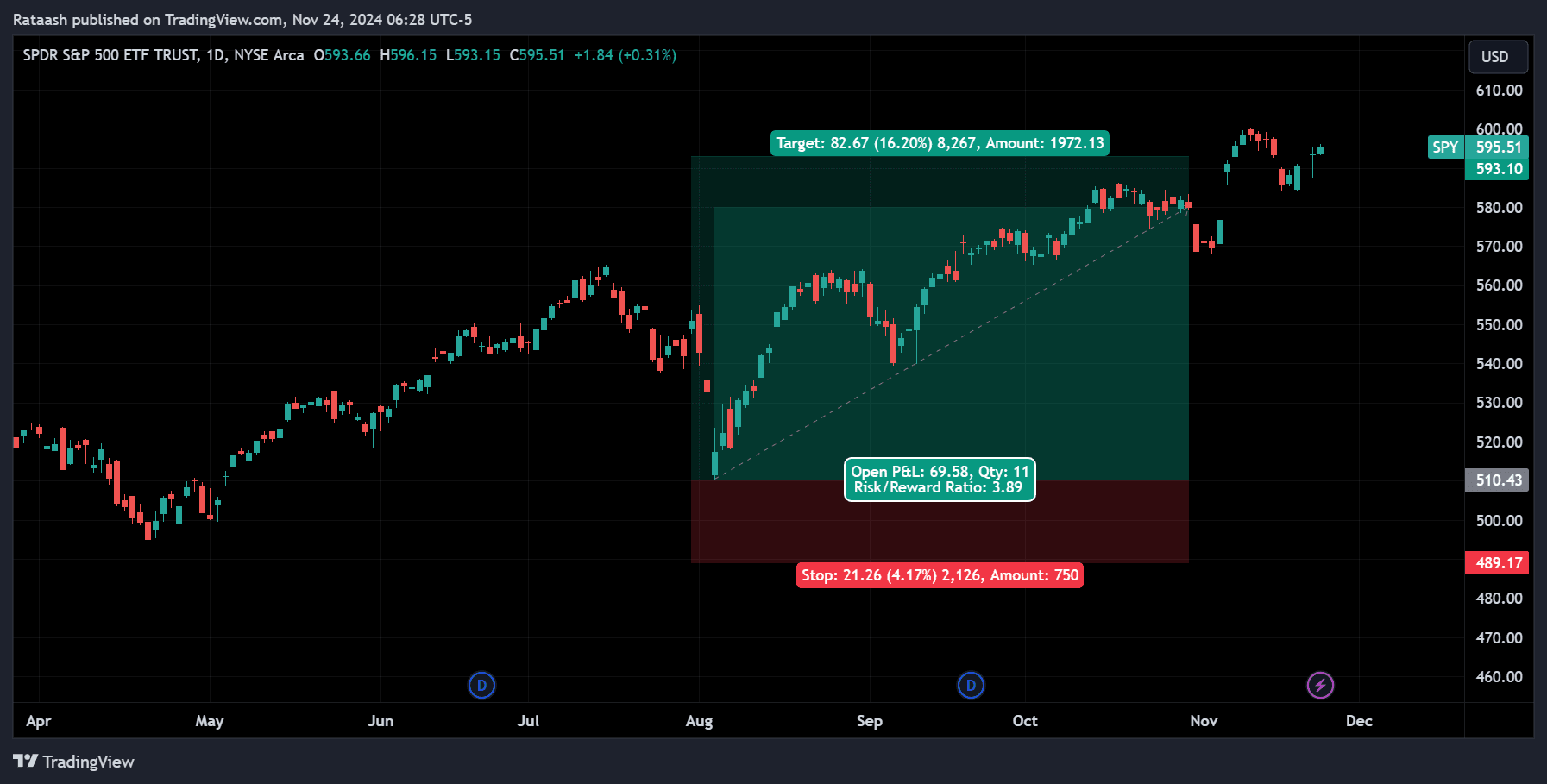
Automatically exit losing trades to prevent large losses.
Diversification:

Avoid opening multiple trades on the same stock or sector simultaneously to reduce overexposure and manage risk effectively.
Action Step: Create a trading plan that includes risk management rules and stick to it, no matter what.
8. Develop Trading Psychology

Trading is as much about managing your emotions as it is about managing your trades. Emotional discipline is essential to avoid impulsive decisions.
Trading psychology is one of the most critical factors in a trader’s success. No matter how skilled you are in technical analysis or risk management, allowing emotions to dictate your decisions can undermine your efforts. Most traders fail not because of a lack of knowledge or strategy, but due to poor control over their trading psychology.
Common Emotional Pitfalls:
- Fear: Holding onto losses for too long.
- Greed: Overtrading or taking excessive risks after a win.
- Overconfidence: Ignoring your trading plan.
Manual Trading and Emotions:
Manually entering trades can intensify emotions. Practice mindfulness techniques and journaling to reflect on your psychological state during trades.
Pro Tip: Take breaks from trading to reset emotionally, especially after big wins or losses.
9. Build and Test Strategies
Profitable trading comes from consistent strategies that fit your style and risk tolerance.
Backtesting:
Test your strategies on historical data to see how they perform in different market conditions.
Demo Trading:
Use a demo account to refine your strategies in real time without risking real money.
Iterate and Improve:
Review your results regularly to identify weaknesses and optimize your approach.
Pro Tip: Use software like NinjaTrader or Amibroker for advanced backtesting.
10. Transition to Live Trading
Once your strategies are tested, start trading with real money. Begin with small positions to gain experience without excessive risk. Gradually scale up as your confidence and results improve.
11. Stay Updated with Market News and Tools
To maintain profitability, stay informed and continuously improve:
Follow Market News:
Use resources like CNBC, MarketWatch, and Reuters for real-time updates.
Leverage Tools:
Use screeners like Finviz to find trading opportunities and trading journals to track your progress.
Continuous Learning:
Read trading books, attend webinars, and follow experienced traders on social media platforms like X and LinkedIn.
Conclusion
Becoming a profitable stock trader is a journey that requires dedication, learning, and discipline. By following this roadmap, you’ll build a strong foundation and develop the skills necessary to succeed. Remember, consistency and patience are your greatest allies in the market. Start today, and let every trade be a step closer to your financial freedom!