
Managing risks in trading is crucial above all else. Without proper risk management, achieving success in trading becomes nearly impossible. Regardless of how much profit you may earn, failure to control losses will prevent you from succeeding.
In this article, we delve into the intricacies of risk management for trading, exploring key concepts, strategies, and best practices to help traders navigate the markets with confidence and resilience.
What is Risk?
Risk is basically an action that has the potential to go wrong. buying a house, buying stocks, or getting married. anything can be risky. we take these risks because the reward associated with them is bigger than the risk.
It’s the same thing in trading. Trading involves the possibility of financial losses, but despite this inherent risk, traders are willing to accept it due to the favorable potential benefits and higher probabilities of making gains.
Instead of blindly assuming risks, it is essential to adopt a systematic approach that allows for a more informed and structured assessment of risk.
Systematic risk and unsystematic risk are two important types of risks that traders encounter in the financial markets.
What is Systematic Risk?
Systematic risk, also known as market risk or undiversifiable risk, refers to risks that affect the overall market or an entire market segment. It is caused by factors that are beyond the control of individual traders or companies.
Systematic risks are inherent in the overall economic, political, or environmental conditions and affect all securities in the market.
Examples of systematic risks include:
- Economic Factors: Economic recessions, inflation, interest rate changes, or currency fluctuations.
- Political Factors: Government policy changes, geopolitical events, or regulatory shifts.
- Market Factors: Market crashes, volatility, or changes in investor sentiment.
- Natural Disasters: Environmental events like hurricanes, earthquakes, or pandemics.
Systematic risks cannot be eliminated through diversification because they are not specific to any particular security or investment.
Instead, traders need to manage systematic risk through strategies like hedging, asset allocation, and adjusting positions based on market conditions.
What is Unsystematic Risk?
Unsystematic risk, also known as specific risk or diversifiable risk, refers to risks that are specific to individual securities, sectors, or companies.
These risks are idiosyncratic and can be mitigated through diversification or some other techniques.
Examples of unsystematic risks include:
- Company-Specific Factors: Poor management decisions, product recalls, or legal issues, CEO resigns
- Industry-Specific Factors: Changes in consumer preferences, technological advancements, or supply chain disruptions.
- Financial Factors: Credit risk of a specific company, liquidity risk, or operational risk.
By diversifying their portfolio across different securities, sectors, or asset classes, traders can reduce unsystematic risk.
This is because unsystematic risks tend to affect only specific securities or groups of securities, and by spreading investments, losses in one area can be offset by gains in another.
We employ these risk mitigation techniques to effectively manage and address the associated risks:
- Risk Acceptance
- Risk Avoidance
- Risk Limitation
- Risk Transference
What is Risk Acceptance?
Risk acceptance refers to the deliberate decision to acknowledge and tolerate a certain level of risk without taking specific actions to mitigate or avoid it.
Traders who choose risk acceptance are willing to bear the potential consequences of risk and are prepared to handle any negative outcomes that may arise.
They understand the potential losses but believe that the potential rewards outweigh the risks involved.
This method, often referred to as “buy and hold,” is commonly utilized by investors.
What is Risk Avoidance?
Risk avoidance involves taking deliberate measures to completely steer clear of certain risks.
Traders who adopt a risk avoidance strategy identify specific risks that they find unacceptable and take proactive steps to avoid exposure to those risks.
This can be achieved by avoiding certain trading activities, markets, or instruments that are associated with the identified risks.
This one is so important in trading and it is something you need to practice to succeed in trading. you need to know when not to take a trade.
What is Risk Limitation?
Risk limitation focuses on implementing measures to minimize the impact or likelihood of risks.
Traders who employ risk limitation strategies aim to reduce the potential losses or negative consequences if a risk event occurs.
This can involve setting stop-loss orders, utilizing protective options strategies, or implementing position sizing techniques to limit exposure to any single trade or risk factor.
What is a Stop-Loss Order?
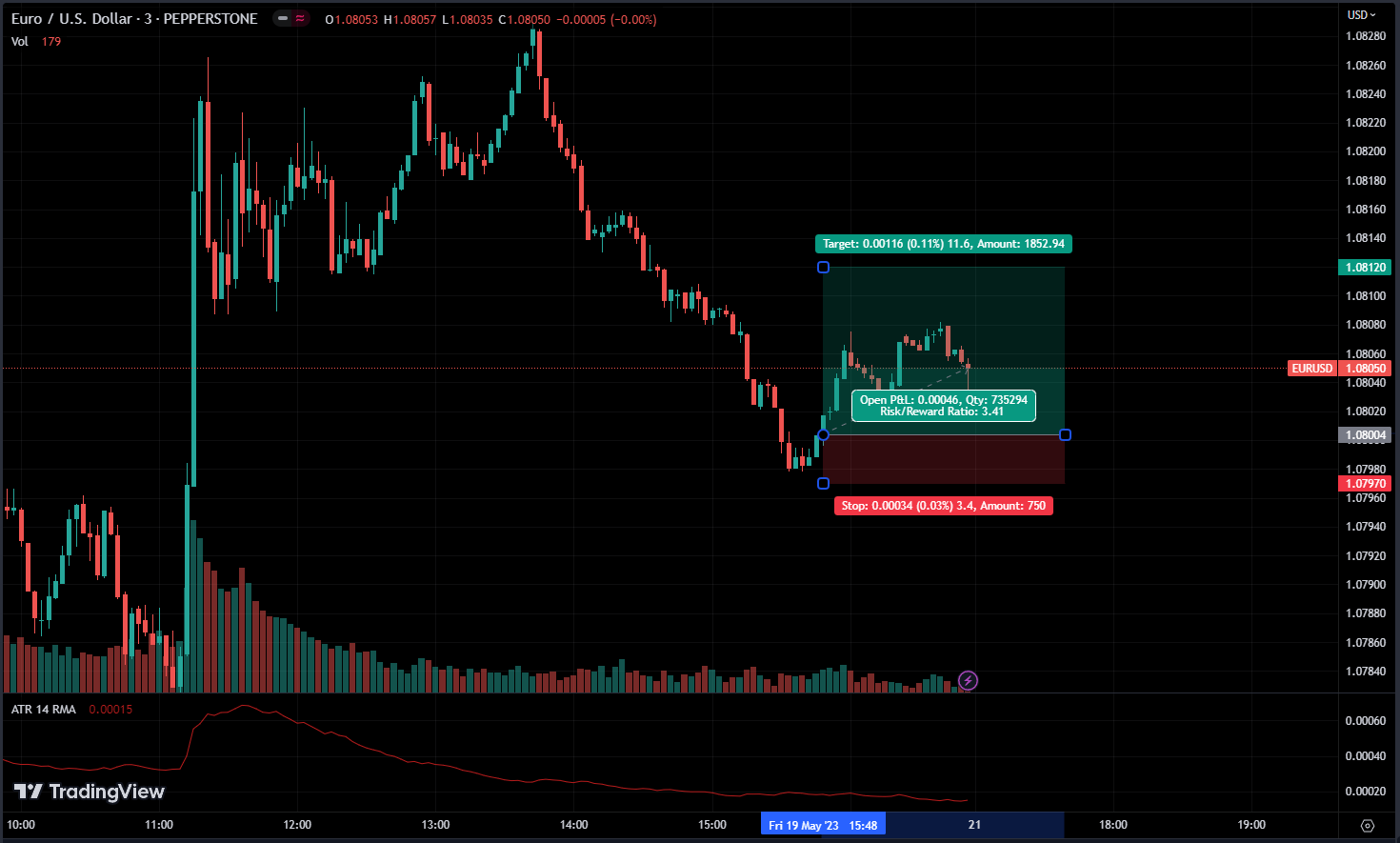
Every single trade should have a stop-loss, Which is a risk limitation.
A stop-loss order is a predetermined instruction given by a trader to their broker or trading platform to automatically sell or buy an asset when it reaches a specific price level, known as the stop price. It’s basically a limit order.
The purpose of a stop-loss order is to protect traders from excessive losses by triggering an automatic exit from a trade if the price moves against their desired direction.
When placing a stop-loss order, traders specify the stop price, which is typically set below the current market price for a short position and above the market price for a long position.
When the market price either reaches or falls below the stop price set for a short position, or reaches or rises above the stop price for a long position, the stop-loss order is triggered. Consequently, the asset is either sold or bought, depending on the type of order specified.
This helps limit losses by ensuring that a trader exits a trade before potential losses become too significant.
Stop-loss orders provide traders with a proactive risk management approach.
They allow traders to define their maximum acceptable loss for a trade in advance and help remove emotions from the decision making process.
By setting a stop-loss order, traders have a predefined exit strategy that can be automatically executed, even if they are not actively monitoring the market.
It’s important to note that stop-loss orders are not foolproof and do not guarantee execution at the specified stop price.
In cases of extreme market volatility or price gaps, the executed price may differ from the stop price, resulting in slippage.
Traders should carefully consider their risk tolerance, market conditions, and individual trading strategies when setting stop-loss levels.
Typically, for short orders, stop-loss levels are often set above resistance, while for long orders, they are commonly placed below support. or some price where you think the asset is unlikely to go.
To get more used to it, try out the TradingView chart and stop-loss tool.
What is Risk Transference?
Risk transference involves shifting or transferring the potential negative impact of a risk to another party or entity.
Traders who opt for risk transference strategies seek to transfer the risk responsibility to a third party, typically through the use of insurance or hedging instruments.
For example, purchasing an insurance policy to protect against losses or using derivatives to transfer market risk to other market participants.
We retail traders almost never use this. but just remember risk transference is a risk mitigation method used in trading.
Why is Risk Management Important in Trading?
Imagine venturing on a road trip without a map or a spare tire. Trading without risk management is like that expedition – fraught with danger and a potential recipe for disaster. Here’s why risk management is paramount:
Limits Losses:
The markets are unpredictable, and losses are inevitable. A sound risk management strategy helps minimize these losses, preventing a single bad trade from wiping out your account.
Protects Capital:
Your capital is your lifeline in the trading world. Risk management safeguards it, allowing you to stay in the game and capitalize on future opportunities.
Boosts Confidence:
Knowing you have a plan in place to manage risk fosters confidence and reduces emotional trading decisions. You can approach the markets with a clear head and a strategic mindset.
Enhances Long-Term Success:
Trading is a marathon, not a sprint. Effective risk management empowers you to survive the inevitable downturns and prosper over time.
Conclusion
Among the various risk mitigation techniques available, the two approaches we will primarily emphasize are risk avoidance and risk limitation. eliminating trades that are not worthy and minimizing your risk on every single trade.
In conclusion, mastering risk management is essential for achieving success and longevity in trading. By understanding the nature of risks, adhering to sound risk management principles, and implementing effective strategies, traders can navigate the complexities of financial markets with confidence and resilience.
Remember, while trading offers opportunities for profit, prudent risk management is the cornerstone of sustainable trading strategies.